Bitcoin is one of the first implementations of a concept called crypto-currency, which was first described in 1998 by Wei Dai on the cypherpunks mailing list. Building upon the notion that money is any object, or any sort of record, accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts in a given country or socio-economic context, Bitcoin is designed around the idea of using cryptography to control the creation and transfer of money, rather than relying on central authorities.
- -If you are interested in learning more about the technical details of Bitcoin it is recommended you start with these documents:
- - -These are the basic features of any Bitcoin-like network.
- -These rules are enforced collectively by the network. While they will not change for Bitcoin, other digital currencies using Bitcoin's technology may change them to suit their needs.
- -The network has been running for more than 45 months yielding to some impressive security features.
- -|
- {% if c.gravatar_id %}
- |
- {% cycle nil, nil, nil, nil, '
Bitcoin is a system of merchants, individuals, a network of participants and software. Together they maintain a mutually co-operating infrastructure without the need for authorities - a decentralised peer-to-peer system. A core layer of the Bitcoin system is the Bitcoin network through which people interact with it using Bitcoin client software. Below we list such software.
-Bitcoin clients are the base level of technology for conducting Bitcoin transactions. Clients usually store a collection of keys on that computer (often termed a wallet). These keys allow you to send and receive payments through the Bitcoin network. Nobody has access to these keys except yourself, and they must be kept secure. This is where clients differ, with ingenious strategies and ongoing research into making a user-friendly and secure client - not an easy task when both goals often conflict!
-{{ client.description }}
-Website: {{ client.url }}
-Platforms:
- {% for platform in client.platforms %}
-  - {% endfor %}
-
- {% endfor %}
-
Bitcoin is one of the first implementations of a concept called crypto-currency, which was first described in 1998 by Wei Dai on the cypherpunks mailing list. Building upon the notion that money is any object, or any sort of record, accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts in a given country or socio-economic context, Bitcoin is designed around the idea of a new form of money that uses cryptography to control its creation and transactions, rather than relying on central authorities.
+In 2009, the first Bitcoin specification and proof of concept was published in a Cryptography mailing list by a member under the pseudonym of Satoshi Nakamoto. Towards the end of 2010 Satoshi left the project saying he had moved on to other things. The creator of Bitcoin never revealed his identity and simply left his invention to the world. The origin and the motivation behind Bitcoin is still today a great source of mystery.
+Since 2010, the Bitcoin community has grown with many developers working on the project. During June and July 2011, Bitcoin suddenly gained media attention leading to a massive buy rally. The resulting bubble slowly deflated through the latter part of 2011 and the value of Bitcoin has since slowly climbed once again back to its 2011 heights.
+On September 27th 2012, the Bitcoin Foundation was created in an effort to standardize, protect, and promote Bitcoin. Today, the Bitcoin economy is developing quickly with new users joining every day.
+ +These are the basic features of any Bitcoin-like network.
+These rules are enforced collectively by the network. While they will not change for Bitcoin, other digital currencies using the same technology may change them to suit their needs.
+The network has been running for more than 45 months, yielding some impressive security features. There has been especially significant growth over the last year. As of February 2013, here are some statistics.
+Bitcoin can be used to build amazing things, or just answer common needs.
+ + The simplest of all payment systems
The simplest of all payment systemsUnless payment needs to be associated with automatic invoices, accepting money is as simple as adding a Bitcoin address to a website as a bitcoin: link or QR code. This very simple setup is within reach of any user and can fulfill the needs of a good range of clients. It's especially suitable for donations.
+ + Many third party APIs
Many third party APIsThere are many third party payment processing services that provide APIs; you don't need to store bitcoins on your server and handle the security that this implies. At the same time, most of these APIs allow you to exchange your Bitcoins into your local currency at competitive costs.
+ + You can be your own financial system
You can be your own financial systemIf you don't use any third party APIs, you can integrate a Bitcoin server directly in your applications, allowing you to become your own bank and payment processor. With all responsibilities that this implies, you can build amazing systems that process Bitcoin transactions with almost no fees.
+ + Bitcoin addresses to track invoices
Bitcoin addresses to track invoicesBitcoin can create as many Bitcoin addresses as you want. So if you were to build a payment system associated with an invoice, you simply need to generate and monitor a Bitcoin address for each payment. You can also use the same addresses once the payment is done.
+ + Most of the security is on client side
Most of the security is on client sideMost of all parts of the security is handled by the the protocol on client and Bitcoin network side. Authenticity is verified through private keys and double-spend through the Bitcoin network. That means, no PCI compliance or fraud detection. We love things that just work, don't we?
+ + Instant transactions and confirmations
Instant transactions and confirmationsA Bitcoin transaction is usually received within a few seconds and confirmed within 10 minutes. Before that, the transaction can be considered authentic but reversible. If you really require instant transaction, it is recommended to ask for a small transaction fee and use a double-spend detection system.
+ + Cheap micro payments
Cheap micro paymentsBitcoin offers the lowest payment processing fees for any type of transaction, including micro-payments. Which means that it can also be used to design and implement new creative online services that could not exist before only because of financial limitations.
diff --git a/en/bitcoin-for-enthusiasts.html b/en/bitcoin-for-enthusiasts.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..ea3a04ce --- /dev/null +++ b/en/bitcoin-for-enthusiasts.html @@ -0,0 +1,27 @@ +--- +layout: base-en +title: Bitcoin for Enthusiasts +--- +Bitcoin is changing the world of finance, making it more open and democratic.
+ + Bitcoin is a worldwide democratic consensus
Bitcoin is a worldwide democratic consensusBy its decentralized open-source nature, Bitcoin is the first payment network that is powered by its users with no central authority. Even Bitcoin developers have no power to force updates in the protocol if enough users, developers, or miners disagree. You have exclusive control over your Bitcoin wallet.
+ + Digital money made for the Internet
Digital money made for the InternetBitcoin is born from the Internet, bringing the freedom of physical money to the virtual world while making payments easier and more secure in both worlds. Bitcoin can offer an alternative to previous cumbersome and costly systems, and it can increase online business access to developing countries.
+ + Protecting individual rights and freedom
Protecting individual rights and freedomBitcoin allows people to securely store and exchange value on a network that cannot be seized, manipulated or stopped by any organization or individual. It gives many powerful tools to the people so that it is easier to protect individual rights against various levels of corruption.
+ + The first global neutral currency
The first global neutral currencyNot often in our history has money been disconnected from any political influence or national economy. Could Bitcoin be the first global currency to cross all barriers between nations, politics and cultures for the benefit of the common good? It certainly looks like it might happen. One for all and all for one!
+ + Promoting transparency
Promoting transparencyAll Bitcoin transactions are public, but the owner or recipients of these transactions are not. Organizations can choose to reveal their ownership of some Bitcoin addresses to their members, allowing them to implement high levels of transparency.
+ + Making money more secure
Making money more secureThanks to a clever use of strict cryptographic rules, Bitcoin provides an amazing list of security features. Not only are bitcoins impossible to counterfeit or spoof, but the protocol is also built to be very resistant against an impressive list of attacks, including distributed denial of service.
+ + Solving issues with trust in banks
Solving issues with trust in banksBitcoin offer solutions to many of the trust problems that plague banks thanks to selective accounting transparency, signature proofs, and irreversible transactions. It also increases the risks for crooked bankers: no bitcoins can be created to save them from their own mistakes at the expense of the people.
diff --git a/en/bitcoin-for-individuals.html b/en/bitcoin-for-individuals.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..d8bb057b --- /dev/null +++ b/en/bitcoin-for-individuals.html @@ -0,0 +1,24 @@ +--- +layout: base-en +title: Bitcoin for Individuals - Bitcoin +--- +Bitcoin is the simplest way to exchange money at very low cost.
+ + Mobile payments made easy
Mobile payments made easyBitcoin on mobiles allows you to pay with a simple two step scan-and-pay. No need to swipe your card, type a PIN or sign anything. And all you need to receive Bitcoin payments is to display the QR code in your Bitcoin wallet app and let your friend scan your mobile, or touch the two phones together (using NFC radio technology).
+ + Fast international payments
Fast international paymentsBitcoins can be transferred from Africa to Canada in 10 minutes. There is no bank to slow down the process, level outrageous fees or freeze the transfer. You can pay your neighbors the same way as you can pay a member of your family in another country.
+ + Works everywhere, anytime
Works everywhere, anytimeJust like with email, you don't need to force your family to use the same software or the same service providers. Just let them stick to their own favorites. No problem there, they are all compatible as they use the same open technology. The Bitcoin network never sleeps, even on holidays!
+ + Secure transactions
Secure transactionsBitcoin transactions are secured by military grade cryptography. Nobody can make a payment on your behalf or charge you money without having a copy of your wallet. So as long as you take required steps to protect your wallet, Bitcoin provides a nice level of protection against many types of fraud.
+ + Almost 100% free to use
Almost 100% free to useYou can already send and receive payments for free! Except for special cases like very tiny micro-payments, there is no enforced fee. You can however choose to pay a small voluntary fee to increase your transaction priority and to remunerate people who operate the Bitcoin network.
+ + Anonymous online payments
Anonymous online paymentsAnonymous payments are a part of our everyday lives as most of real life purchases are done without the requirement to provide a proper identification. Bitcoin now introduces the same freedom to the online world. It allows you to buy services or make donations without the hassle of being passed under x-ray. However, you should note that full anonymity requires special efforts.
diff --git a/en/bitcoin-for-organizations.html b/en/bitcoin-for-organizations.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..7655b75c --- /dev/null +++ b/en/bitcoin-for-organizations.html @@ -0,0 +1,30 @@ +--- +layout: base-en +title: Bitcoin for Organizations - Bitcoin +--- +Bitcoin is a very secure and inexpensive way to handle payments.
+ + The lowest fees out there
The lowest fees out thereBitcoin's high cryptographic security allows it to process transactions in a very efficient and inexpensive way. You can make and receive payments using the Bitcoin network with zero fees in most cases. You can pay a very small voluntary fee if you want to increase a transaction's priority.
+ + Protection against payment and chargeback fraud
Protection against payment and chargeback fraudAny business that accepts credit card or PayPal payments knows the problem of payments that are later reversed because the sender's account was hacked or they fraudulently claim non-delivery. The only way businesses can defend themselves against this kind of fraud is with complex risk analysis and increased prices to cover the losses. Bitcoin payments are irreversible and wallets can be kept highly secure, meaning that the cost of theft is no longer pushed onto the shoulders of merchants.
+ + Fast international payments
Fast international paymentsBitcoins can be transferred from Africa to Canada in 10 minutes. In fact, Bitcoins never have any real physical location. So you can transfer as many of them as you want anywhere with no limits, delays or excessive fees. There are no intermediate banks to make you wait three business days.
+ + No PCI compliance required
No PCI compliance requiredAccepting credit cards online typically requires extensive security checks in order to comply with the PCI standard. While it is a good thing to protect credit cards, Bitcoin security is built in such a way that makes this approach obsolete. Your payments are secured by the network, not at your expense.
+ + Instant transactions for points-of-sale
Instant transactions for points-of-saleA Bitcoin transaction is usually deployed within a few seconds and confirmed within 10 minutes. Before that, the transaction can be considered authentic but reversible. If you really require instant transactions, it is recommended to ask for a small transaction fee and use a double-spend detection system.
+ + Get some free visibility
Get some free visibilityBitcoin is an emerging market of new customers who are searching ways to spend their coins. Accepting them is a good way to get new customers and give your business some new visibility. Accepting a new payment method has always shown to be a clever practice for online businesses.
+ + Multi-signature
Multi-signatureBitcoin also includes a feature that is not yet well known, allowing coins to be spent only if a subset of a group of people sign the transaction (so-called "n of m" transactions). This is the equivalent of the good old multi-signature cheque system that you might still use with banks today.
+ + Accounting transparency
Accounting transparencyMany organizations are required to produce accounting documents about their activity and to adopt good transparency practices. Using Bitcoin offers the highest level of transparency since your balance and your transactions are public for your members if you keep them aware of your Bitcoin addresses.
diff --git a/en/choose-your-wallet.html b/en/choose-your-wallet.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..cd74e6fa --- /dev/null +++ b/en/choose-your-wallet.html @@ -0,0 +1,105 @@ +--- +layout: base-en +title: Choose your wallet - Bitcoin +--- + + + +Your Bitcoin wallet is what allows you to transact with the world. It gives you ownership of Bitcoin addresses that you can use to receive coins from other users, and then lets you send those coins onwards. Just like email, you can receive Bitcoins when you are offline and all wallets are compatible with each other.
+If you are new to Bitcoin, those wallets are a good place to begin.
+Do you have a computer that you keep switched on all the time, that's connected to the internet? You can help the community by simply running the original Bitcoin client on it. The original client is more resource intensive and will take a complete day to synchronize. After that your computer will contribute to the network by checking and relaying transactions.
 Software wallets
Software walletsSoftware wallets are installed on your computer. They give you complete control of your wallet. You are responsible for doing backups and protecting your money. Just like cash.
+ + +


Bitcoin-Qt is the original Bitcoin client and it builds the backbone of the network. It offers the highest levels of security, privacy and stability. However it has fewer features and it takes a lot of space and memory.
+ + + +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ 


Multibit is a lightweight client that focuses on being fast and easy to use. It synchronizes with the network and is ready to use in minutes. Multibit also supports many languages. It is a good choice for non-technical users.
+ + + +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ 

Armory is an advanced Bitcoin client that runs on top of Bitcoin-Qt. Expanding its features for Bitcoin power users. It offers many backup and encryption features, and it allows secure cold-storage on offline computers.
+ + + +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ 



Electrum's focus is speed and simplicity, with low resource usage. It uses remote servers that handle the most complicated parts of the Bitcoin system, and it allows you to recover your wallet from an encrypted online backup.
+ + + +
+
+
+ Mobile wallets
Mobile walletsMobile wallets allow you to bring Bitcoin with you in your pocket. You can exchange coins easily and pay in physical stores by scanning a QR code or using NFC "tap to pay".
+ + +
Bitcoin wallet is a lightweight mobile client that is available for Android phones and tablets. This client does not need to be associated with any online service to work. It is compatible with QR Code scanning and NFC.
+ + + +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ 

Blockchain is a mobile online wallet powered by blockchain.info. It is also available for iPhones in a restricted mode to fits Apple policies. It includes many blockchain.info features like online wallet backup.
+ + + +
+
+
+ Online wallets
Online walletsOnline wallets allow you to use your Bitcoin anywhere with less do to protect them. However, you must choose your online wallet with care as they host your Bitcoins.
+ + +Blockchain is a user-friendly web wallet. It stores an encrypted version of your wallet online but decryption only happens in your browser. For security reasons, you should always use the browser extension and email backups.
+ + + +
+
+
+If you are interested in learning more about the technical details of Bitcoin it is recommended you start with these documents.
+ + +Bitcoin development is open source and any developer can contribute to the project. Everything you need is in the Github repository. Please make sure to read and follow the development process described in the README as well as to provide good quality code and respect all guidelines.
+ +(Ordered by number of commits)
+|
+ {% if c.gravatar_id %}
+ |
+ {% cycle nil, nil, nil, nil, '
+ Download for Windows (zip) ~13MB
Download for Windows (zip) ~13MB
+ Download for Windows (exe) ~9MB
Download for Windows (exe) ~9MB
+ Download for Ubuntu (PPA)
Download for Ubuntu (PPA)
+ Download for Linux (tgz, 32/64-bit) ~12MB
Download for Linux (tgz, 32/64-bit) ~12MB
+ Download for Mac OS X ~13MB
Download for Mac OS X ~13MB
+ Source code (GitHub)
+ Show version history
+
Bitcoin-Qt is a community-driven free open source project, released under the MIT license.
+Note : Bitcoin-Qt initial sync can take a day to complete. You should make sure that you have enough bandwidth and storage for the full blockchain size.
+ diff --git a/en/faq.html b/en/faq.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..2dda2d66 --- /dev/null +++ b/en/faq.html @@ -0,0 +1,340 @@ +--- +layout: base-en +title: Frequently Asked Questions +--- +Bitcoins are the unit of currency of the Bitcoin system. A commonly used shorthand for this is “BTC” to refer to a price or amount (eg: “100 BTC”).
+There are such things as physical bitcoins, but ultimately, a bitcoin is just a number associated with a Bitcoin address. A physical bitcoin is simply an object, such as a coin, with the number carefully embedded inside. See also an Introduction to bitcoin.
+ +There are a variety of ways to acquire bitcoins:
++Since Bitcoin is a new technology, what it is and how it works may be initially unclear. Bitcoin is sometimes presented as being one of three things: +
++In fact, none of the above are true. Let's look at them independently. +
+ +If you've spent much time on the Internet, you've probably seen ads for many 'get-rich-quick' schemes. These ads usually promise huge profits for a small amounts of easy work. Such schemes are usually pyramid/matrix-style schemes that make money from their own employees and offer nothing of any real value. Most convince one to buy packages that will make them earn hundreds a day, which in fact have the buyer distribute more such ads, and make minute profits.
+ +Bitcoin is in no way similar to these schemes. Bitcoin doesn't promise windfall profits. There is no way for the developers to make money from your involvement or to take money from you. That bitcoins are nearly impossible to acquire without the owner's consent represents one of its greatest strengths. Bitcoin is an experimental, virtual currency that may succeed or may fail. None of its developers expect to get rich off of it.
+ +A more detailed answer to this question can be found here.
+ +Most people who use Bitcoin don't earn anything by doing so, and the default client has no built-in way to earn Bitcoins. A small minority of people with dedicated, high-performance hardware do earn some Bitcoins by "mining" (generating new bitcoins, see [[#What is mining?|What is mining?]]) with special software, but joining Bitcoin shouldn't be construed as being the road to riches. Most Bitcoin users get involved because they find the project conceptually interesting and don't earn anything by doing so. This is also why you won't find much speculation about the political or economic repercussions of Bitcoin anywhere on this site: Bitcoin developers owe their dedication to the project's intellectual yieldings more than to those of a monetary nature. Bitcoin is still taking its first baby steps; it may go on to do great things but right now it only has something to offer those chasing conceptually interesting projects or bleeding edge technology. +
+ +Bitcoin is a new and interesting electronic currency, the value of which is not backed by any single government or organization. Like other currencies, it is worth something partly because people are willing to trade it for goods and services. Its exchange rate fluctuates continuously, and sometimes wildly. It lacks wide acceptance and is vulnerable to manipulation by parties with modest funding. Security incidents such as website and account compromise may trigger major sell-offs. Other fluctuations can build into positive feedback loops cause much larger exchange rate fluctuations. Anyone who puts money into Bitcoin should take measures to reduce their risk and consider it as a high-risk currency. Later, as Bitcoin becomes better known and more widely accepted, it should stabilize, but for the time being it is unpredictable. Any investment in Bitcoin should be done carefully and with a clear plan to manage risk.
+ +
It is possible to buy physical bitcoins with PayPal but it is otherwise difficult and/or expensive to do so, because of significant risk to the seller.
+While it is possible to find an individual who wishes to sell Bitcoin to you via Paypal, (perhaps via #bitcoin-otc ) most exchanges do not allow funding through PayPal. This is due to repeated cases where someone pays for bitcoins with Paypal receives their bitcoins, and then fraudulently complains to Paypal that they never received their purchase. PayPal often sides with the fraudulent buyer in this case which means any seller would need to cover that risk with higher fees or refuse to accept PayPal altogether.
+Buying Bitcoins from individuals with this method is still possible, but requires the seller to have some trust that the buyer will not file a claim with PayPal to reverse the payment.
+ + +
+Total Bitcoins over time
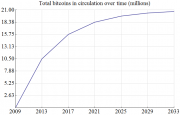
+New bitcoins are generated by the network through the process of mining. In a process that is similar to a continuous raffle draw, mining nodes on the network are awarded bitcoins each time they find the solution to a certain mathematical problem (and thereby create a new block). Creating a block is a proof of work with a difficulty that varies with the overall strength of the network. The reward for solving a block is automatically adjusted so that in roughly the first four years of operation of the Bitcoin network, {{formatnum:10500000}} BTC will be created. This amount is halved each four years, so it will be {{formatnum:5250000}} over years 4-8, {{formatnum:2625000}} over years 8-12, and so on. Thus the total number of bitcoins in existence will not exceed {{formatnum:21000000}}. See Controlled Currency Supply.
+Blocks are mined every 10 minutes, on average and for the first four years ({{formatnum:210000}} blocks) each block includes 50 new bitcoins. As the amount of processing power directed at mining changes, the difficulty of creating new bitcoins changes. This difficulty factor is calculated every 2016 blocks and is based upon the time taken to generate the previous 2016 blocks. See Mining.
+ +Current count. Also see Total bitcoins in circulation chart
+The number of blocks times the coin value of a block is the number of coins in existence. The coin value of a block is 50 BTC for each of the first {{formatnum:210000}} blocks, 25 BTC for the next {{formatnum:210000}} blocks, then 12.5 BTC, 6.25 BTC and so on.
+ +A bitcoin can be divided down to 8 decimal places. Therefore, 0.00000001 BTC is the smallest amount that can be handled in a transaction. If necessary, the protocol and related software can be modified to handle even smaller amounts.
+ +There is a lot of discussion about the naming of these fractions of bitcoins. The leading candidates are:
+The above follows the accepted international SI prefixes for hundredths, thousandths, and millionths. There are many arguments against the special case of 0.01 BTC since it is unlikely to represent anything meaningful as the Bitcoin economy grows (it certainly won't be the equivalent of 0.01 USD, GBP or EUR). Equally, the inclusion of existing national currency denominations such as "cent", "nickel", "dime", "pence", "pound", "kopek" and so on are to be discouraged; this is a worldwide currency.
+One exception is the "satoshi" which is smallest denomination currently possible
+which is so named in honour of Satoshi Nakamoto, the pseudonym of the inventor of Bitcoin.
+For an overview of all defined units of Bitcoin (including less common and niche units), see Units.
+Further discussion on this topic can be found on the forums here:
+ + +Eventually the reward will go from 0.00000001 BTC to zero and no more bitcoins will be created.
+The block reward calculation is done as a right bitwise shift of a 64-bit signed integer, which means it is divided by two and rounded down. The integer is equal to the value in BTC * 100,000,000 since internally in the reference client software, all Bitcoin balances and values are stored as unsigned integers.
+With an initial block reward of 50 BTC, it will take many 4-year periods for the block reward to reach zero.
+ +The last block that will generate coins will be block #6,929,999 which should be generated at or near the year 2140. The total number of coins in circulation will then remain static at 20,999,999.9769 BTC.
+Even if the allowed precision is expanded from the current 8 decimals, the total BTC in circulation will always be slightly below 21 million (assuming everything else stays the same). For example, with 16 decimals of precision, the end total would be 20,999,999.999999999496 BTC.
+ +Absolutely! Even before the creation of coins ends, the use of transaction fees will likely make creating new blocks more valuable from the fees than the new coins being created. When coin generation ends, these fees will sustain the ability to use bitcoins and the Bitcoin network. There is no practical limit on the number of blocks that will be mined in the future.
+ +Because of the law of supply and demand, when fewer bitcoins are available the ones that are left will be in higher demand, and therefore will have a higher value. So, as Bitcoins are lost, the remaining bitcoins will eventually increase in value to compensate. As the value of a bitcoin increases, the number of bitcoins required to purchase an item '''de'''creases. This is a deflationary economic model. As the average transaction size reduces, transactions will probably be denominated in sub-units of a bitcoin such as millibitcoins ("Millies") or microbitcoins ("Mikes").
+The Bitcoin protocol uses a base unit of one hundred-millionth of a Bitcoin ("a Satoshi"), but unused bits are available in the protocol fields that could be used to denote even smaller subdivisions.
+ +The Bitcoin protocol allows lightweight clients that can use Bitcoin without downloading the entire transaction history. As traffic grows and this becomes more critical, implementations of the concept will be developed. Full network nodes will at some point become a more specialized service.
+With some modifications to the software, full Bitcoin nodes could easily keep up with both VISA and MasterCard combined, using only fairly modest hardware (a single high end server by todays standards). It is worth noting that the MasterCard network is structured somewhat like Bitcoin itself - as a peer to peer broadcast network.
+Learn more about Scalability.
+ +Bitcoins have value because they are useful and because they are scarce. As they are accepted by more merchants, their value will stabilize. See the list of Bitcoin-accepting sites.
+When we say that a currency is backed up by gold, we mean that there's a promise in place that you can exchange the currency for gold. Bitcoins, like dollars and euros, are not backed up by anything except the variety of merchants that accept them.
+It's a common misconception that Bitcoins gain their value from the cost of electricity required to generate them. Cost doesn't equal value – hiring 1,000 men to shovel a big hole in the ground may be costly, but not valuable. Also, even though scarcity is a critical requirement for a useful currency, it alone doesn't make anything valuable. For example, your fingerprints are scarce, but that doesn't mean they have any exchange value.
+Alternatively it needs to be added that while the law of supply and demand applies it does not guarantee value of Bitcoins in the future. If confidence in Bitcoins is lost then it will not matter that the supply can no longer be increased, the demand will fall off with all holders trying to get rid of their coins. An example of this can be seen in cases of state currencies, in cases when the state in question dissolves and so no new supply of the currency is available (the central authority managing the supply is gone), however the demand for the currency falls sharply because confidence in its purchasing power disappears. Of-course Bitcoins do not have such central authority managing the supply of the coins, but it does not prevent confidence from eroding due to other situations that are not necessarily predictable.
+ +Yes, in the same way as the euro and dollar are. They only have value in exchange and have no inherent value. If everyone suddenly stopped accepting your dollars, euros or bitcoins, the "bubble" would burst and their value would drop to zero. But that is unlikely to happen: even in Somalia, where the government collapsed 20 years ago, Somali shillings are still accepted as payment.
+ +In a Ponzi Scheme, the founders persuade investors that they’ll profit. Bitcoin does not make such a guarantee. There is no central entity, just individuals building an economy.
+A ponzi scheme is a zero sum game. Early adopters can only profit at the expense of late adopters. Bitcoin has possible win-win outcomes. Early adopters profit from the rise in value. Late adopters, and indeed, society as a whole, benefit from the usefulness of a stable, fast, inexpensive, and widely accepted p2p currency.
+The fact that early adopters benefit more doesn't alone make anything a Ponzi scheme. All good investments in successful companies have this quality.
+ +Early adopters have a large number of bitcoins now because they took a risk and invested resources in an unproven technology. By so doing, they have helped Bitcoin become what it is now and what it will be in the future (hopefully, a ubiquitous decentralized digital currency). It is only fair they will reap the benefits of their successful investment.
+In any case, any bitcoin generated will probably change hands dozens of time as a medium of exchange, so the profit made from the initial distribution will be insignificant compared to the total commerce enabled by Bitcoin.
+Since the pricing of Bitcoins has fallen greatly from its June 2011 peak, prices today are much more similar to those enjoyed by many early adopters. Those who are buying Bitcoins today likely believe that Bitcoin will grow significantly in the future. Setting aside the brief opportunity to have sold Bitcoins at the June 2011 peak enjoyed by few, the early-adopter window is arguably still open.
+ +Worries about Bitcoin being destroyed by deflation are not entirely unfounded. Unlike most currencies, which experience inflation as their founding institutions create more and more units, Bitcoin will likely experience gradual deflation with the passage of time. Bitcoin is unique in that only a small amount of units will ever be produced (twenty-one million to be exact), this number has been known since the project's inception, and the units are created at a predicable rate.
+Also, Bitcoin users are faced with a danger that doesn't threaten users of any other currency: if a Bitcoin user loses his wallet, his money is gone forever, unless he finds it again. And not just to him; it's gone completely out of circulation, rendered utterly inaccessible to anyone. As people will lose their wallets, the total number of Bitcoins will slowly decrease.
+Therefore, Bitcoin seems to be faced with a unique problem. Whereas most currencies inflate over time, Bitcoin will mostly likely do the just the opposite. Time will see the irretrievable loss of an ever-increasing number of Bitcoins. An already small number will be permanently whittled down further and further. And as there become fewer and fewer Bitcoins, the laws of supply and demand suggest that their value will probably continually rise.
+Thus Bitcoin is bound to once again stray into mysterious territory, because no one exactly knows what happens to a currency that grows continually more valuable. Economists generally agree that a low level of inflation is a good thing for a currency, but nobody is quite sure about what might happens to one that continually deflates. Although deflation could hardly be called a rare phenomenon, steady, constant deflation is unheard of. There may be a lot of speculation, no one has any hard data to back up their claims.
+That being said, there is a mechanism in place to combat the obvious consequences. Extreme deflation would render most currencies highly impractical: if a single Canadian dollar could suddenly buy the holder a car, how would one go about buying bread or candy? Even pennies would fetch more than a person could carry. Bitcoin, however, offers a simple and stylish solution: infinite divisibility. Bitcoins can be divided up and trade into as small of pieces as one wants, so no matter how valuable Bitcoins become, one can trade them in practical quantities.
+In fact, infinite divisibility should allow Bitcoins to function in cases of extreme wallet loss. Even if, in the far future, so many people have lost their wallets that only a single Bitcoin, or a fraction of one, remains, Bitcoin should continue to function just fine. No one can claim to be sure what is going to happen, but deflation may prove to present a smaller threat than many expect.
+For more information, see the Deflationary spiral page.
+ +Bitcoin markets are competitive -- meaning the price of a bitcoin will rise or fall depending on supply and demand at certain price levels. Only a fraction of bitcoins issued to date are found on the exchange markets for sale. So even though technically a buyer with lots of money could buy all the bitcoins offered for sale, unless those holding the rest of the bitcoins offer them for sale as well, even the wealthiest, most determined buyer can't get at them.
+Additionally, new currency continues to be issued daily and will continue to do so for decades though over time the rate at which they are issued declines to insignificant levels. Those who are mining aren't obligated to sell their bitcoins so not all bitcoins will make it to the markets even.
+This situation doesn't suggest, however, that the markets aren't vulnerable to price manipulation. It doesn't take significant amounts of money to move the market price up or down and thus Bitcoin remains a volatile asset.
+ +That the block chain cannot be easily forked represents one of the central security mechanisms of Bitcoin. Given the choice between two block chains, a Bitcoin miner always chooses the longer one - that is to say, the one with the more complex hash. Thusly, it ensures that each user can only spend their bitcoins once, and that no user gets ripped off.
+As a consequence of the block chain structure, there may at any time be many different sub-branches, and the possibility always exists of a transaction being over-written by the longest branch, if it has been recorded in a shorter one. The older a transaction is though, the lower its chances of being over-written, and the higher of becoming permanent. Although the block chain prevents one from spending more Bitcoins than one has, it means that transactions can be accidentally nullified.
+A new block chain would leave the network vulnerable to double-spend attacks. However, the creation of a viable new chain presents considerable difficulty, and the possibility does not present much of a risk.
+Bitcoin will always choose the longer Block Chain and determines the relative length of two branches by the complexities of their hashes. Since the hash of each new block is made from that of the block preceding it, to create a block with a more complex hash, one must be prepared to do more computation than has been done by the entire Bitcoin network from the fork point up to the newest of the blocks one is trying to supersede. Needless to say, such an undertaking would require a very large amount of processing power and since Bitcoin is continually growing and expanding, it will likely only require more with the passage of time.
+A much more distinct and real threat to the Bitcoin use is the development of other, superior virtual currencies, which could supplant Bitcoin and render it obsolete and valueless.
+A great deal of careful thought and ingenuity has gone into the development of Bitcoin, but it is the first of its breed, a prototype, and vulnerable to more highly-evolved competitors. At present, any threatening rivals have yet to rear its head; Bitcoin remains the first and foremost private virtual currency, but we can offer no guarantees that it will retain that position. It would certainly be in keeping with internet history for similar system built from the same principles to supersede and cast Bitcoin into obsolescence, after time had revealed its major shortcomings. Friendster and Myspace suffered similar fates at the hand of Facebook, Napster was ousted by Limeware, Bearshare and torrent applications, and Skype has all but crushed the last few disciples of the Microsoft Messenger army.
+This may sound rather foreboding, so bear in mind that introduction of new and possibly better virtual currencies will not necessarily herald Bitcoin's demise. If Bitcoin establishes itself sufficiently firmly before the inception of the next generation of private, online currencies as to gain widespread acceptance and general stability, future currencies may pose little threat even if they can claim superior design.
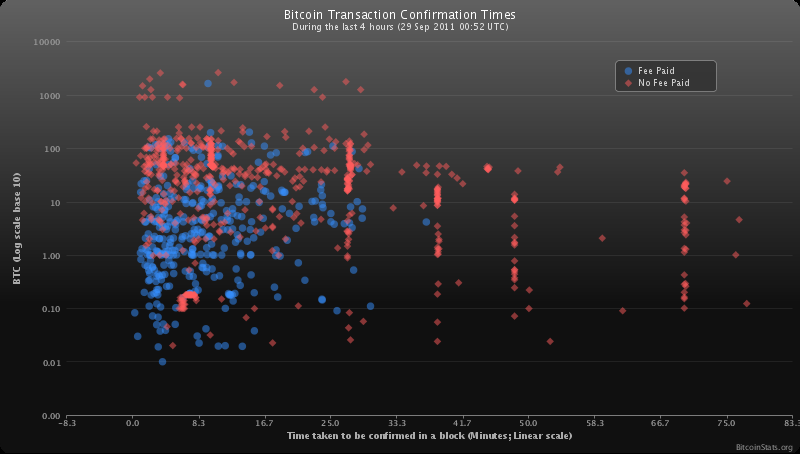
+ +10 minutes is the average time taken to find a block. It can be significantly more or less time than that depending on luck; 10 minutes is simply the average case.
+You can see how long all other recent transactions have taken here: BitcoinStats.org.
+Blocks (shown as "confirmations" in the GUI) are how the Bitcoin achieves consensus on who owns what. Once a block is found everyone agrees that you now own those coins, so you can spend them again. Until then it's possible that some network nodes believe otherwise, if somebody is attempting to defraud the system by reversing a transaction. The more confirmations a transaction has, the less risk there is of a reversal. Only 6 blocks or 1 hour is enough to make reversal computationally impractical. This is dramatically better than credit cards which can see chargebacks occur up to three months after the original transaction!
+Ten minutes was specifically chosen by Satoshi as a tradeoff between propagation time of new blocks in large networks and the amount of work wasted due to chain splits. For a more technical explanation, see Satoshi's original technical paper.
+ +
+
+
+YES, you do, IF the transaction is non-recourse. The Bitcoin reference software does not display transactions as confirmed until six blocks have passed (confirmations). As transactions are burred in the chain they become increasingly non-reversible but are very reversible before the first confirmation. Two to six confirmations are recommended for non-recourse situations depending on the value of the transactions involved.
+When people ask this question they are usually thinking about applications like supermarkets. This generally is a recourse situation: if somebody tries to double-spend on a face-to-face transaction it might work a few times, but probabalistically speaking eventually one of the double-spends will get noticed, and the penalty for shoplifting charges in most localities is calibrated to be several times worse than the proceeds of a single shoplifting event.
+Double-spends might be a concern for something like a snack machine in a low-traffic area with no nearby security cameras. Such a machine shouldn't honor 0-confirmation payments, and should instead use some other mechanism of clearing Bitcoin or validating transactions against reversal, see the wiki article here for alternatives.
+Applications that require immediate payment processing, like supermarkets or snack machines, need to manage the risks. Here is one way to reverse an unconfirmed payment:
+A Finney attack, in which an attacker mines a block containing a movement of some coins back to themselves. Once they find a block solution, they quickly go to a merchant and make a purchase, then broadcast the block, thus taking back the coins. This attack is a risk primarily for goods that are dispatched immediately, like song downloads or currency trades. Because the attacker can't choose the time of the attack, it isn't a risk for merchants such as supermarkets where you can't choose exactly when to pay (due to queues, etc). The attack can fail if somebody else finds a block containing the purchasing transaction before you release your own block, therefore, merchants can reduce but not eliminate the risk by making purchasers wait some length of time that's less than a confirm.
+Because pulling off this attack is not trivial, merchants who need to sell things automatically and instantly are most likely to just price the cost of reversal fraud in, or use insurance.
+ +Don't panic! There are a number of reasons why your bitcoins might not show up yet, and a number of ways to diagnose them.
+The latest version of the Bitcoin-Qt client tells you how far it has yet to go in downloading the blockchain. Hover over the icon in the bottom right corner of the client to learn your client's status.
+If it has not caught up then it's possible that your transaction hasn't been included in a block yet.
+You can check pending transactions in the network by going here and then searching for your address. If the transaction is listed here then it's a matter of waiting until it gets included in a block before it will show in your client.
+If the transaction is based on a coin that was in a recent transaction then it could be considered a low priority transaction. Transfers can take longer if the transaction fee paid was not high enough. If there is no fee at all the transfer can get a very low priority and take hours or even days to be included in a block.
+ +Whenever the address listed in "Your address" receives a transaction, Bitcoin replaces it with a new address. This is meant to encourage you to use a new address for every transaction, which enhances anonymity. All of your old addresses are still usable: you can see them in ''Settings -> Your Receiving Addresses''.
+ +Some transactions might require a transaction fee for them to get confirmed in a timely manner. The transaction fee is processed by and received by the bitcoin miner. The most recent version of the Bitcoin client will estimate an appropriate fee when a fee might be required.
+The fee is added to the payment amount. For example, if you are sending a 1.234 BTC payment and the client requires a 0.0005 BTC fee, then 1.2345 BTC will be subtracted from the wallet balance for the entire transaction and the address for where the payment was sent will receive a payment of 1.234 BTC.
+A fee might be imposed because your transaction looks like a denial of service attack to the Bitcoin system. For example, it might be burdensome to transmit or it might recycle Bitcoins you recently received. The wallet software attempts to avoid generating burdensome transactions, but it isn't always able to do so: The funds in your wallet might be new or composed of many tiny payments.
+Because the fee is related to the amount of data that makes up the transaction and not to the amount of Bitcoins being sent, the fee may seem extremely low (0.0005 BTC for a 1,000 BTC transfer) or unfairly high (0.004 BTC for a 0.02 BTC payment, or about 20%). If you are receiving tiny amounts (''e.g.'' as small payments from a mining pool) then fees when sending will be higher than if your activity follows the pattern of conventional consumer or business transactions.
+As of Bitcoin 0.5.3 the required fee will not be higher than 0.05 BTC. For most users there is usually no required fee at all. If a fee is required it will most commonly be 0.0005 BTC.
+ +Bitcoins are not actually "sent" to your wallet; the software only uses that term so that we can use the currency without having to learn new concepts. Your wallet is only needed when you wish to spend coins that you've received.
+If you are sent coins when your wallet client program is not running, and you later launch the wallet client program, the coins will eventually appear as if they were just received in the wallet. That is to say, when the client program is started it must download blocks and catch up with any transactions it did not already know about.
+ +The popular Bitcoin client software from bitcoin.org implements a "full" Bitcoin node: It can carry out all the duties of the Bitcoin P2P system, it isn't simply a "client". One of the principles behind the operation of full Bitcoin nodes is that they don't assume that the other participants have followed the rules of the Bitcoin system. During synchronization, the software is processing historical Bitcoin transactions and making sure for itself that all of the rules of the system have been correctly followed.
+In normal operation, after synchronizing, the software should use a hardly noticeable amount of your computer's resources.
+When the wallet client program is first installed, its initial validation requires a lot of work from your computer's hard disk, so the amount of time to synchronize depends on your disk speed and, to a lesser extent, your CPU speed. It can take anywhere from a few hours to a day or so. On a slow computer it could take more than 40 hours of continuous synchronization, so check your computer's power-saving settings to ensure that it does not turn its hard disk off when unattended for a few hours. You can use the Bitcoin software during synchronization, but you may not see recent payments to you until the client program has caught up to the point where those transactions happened.
+If you feel that this process takes too long, you can download a pre-synchronized blockchain from http://eu2.bitcoincharts.com/blockchain/. Alternatively, you can try an alternative "lite" client such as Multibit or a super-light client like electrum, though these clients have somewhat weaker security, are less mature, and don't contribute to the health of the P2P network.
+ +Bitcoin will connect to other nodes, usually on TCP port 8333. You will need to allow outgoing TCP connections to port 8333 if you want to allow your Bitcoin client to connect to many nodes. Testnet uses TCP port 18333 instead of 8333.
+If you want to restrict your firewall rules to a few IPs, you can find stable nodes in the fallback nodes list.
+ +Bitcoin finds peers primarily by forwarding peer announcements within its own network and each node saves a database of peers that it's aware of, for future use. In order to bootstrap this process Bitcoin needs a list of initial peers, these can be provided manually but normally it obtains them by querying a set of DNS domain names which have automatically updated lists, if that doesn't work it falls back to a build-in list which is updated from time to time in new versions of the software. There is also an IRC based mechanism but it is disabled by default.
+ +Technically speaking, mining is the calculation of a hash of the a block header, which includes among other things a reference to the previous block, a hash of a set of transactions and a nonce. If the hash value is found to be less than the current target (which is inversely proportional to the difficulty), a new block is formed and the miner gets the newly generated Bitcoins (25 per block at current levels). If the hash is not less than the current target, a new nonce is tried, and a new hash is calculated. This is done millions of times per second by each miner.
+ +The computations done when mining are internal to Bitcoin and not related to any other distributed computing projects. They serve the purpose of securing the Bitcoin network, which is useful.
+ +Spending energy on creating and securing a free monetary system is hardly a waste. Also, services necessary for the operation of currently widespread monetary systems, such as banks and credit card companies, also spend energy, arguably more than Bitcoin would.
+ +To provide security for the Bitcoin network, the calculations involved need to have some very specific features. These features are incompatible with leveraging the computation for other purposes.
+ +The incentive for miners to include transactions is in the fees that come along with them. If we were to implement some minimum number of transactions per block it would be trivial for a miner to create and include transactions merely to surpass that threshold. As the network matures, the block reward drops, and miners become more dependent on transactions fees to pay their costs, the problem of zero transaction blocks should diminish over time.
+ +To give a general idea of the mining process, imagine this setup:
+
+ payload = [some data related to things happening on the Bitcoin network]
+ nonce = 1
+ hash = SHA2( SHA2( payload + nonce ) )
+
The cost function use in bitcoin is the Hashcash cost-function. Bit coin mining intensively computes a high value Hashcash stamp on the underlying block chain data. The hashcash stamp that Bitcoin miners produce is computed by repeatedly increasing "nonce" until the hash function yields a value, that has the rare property of being below a certain target threshold. (In other words: The hash "starts with a certain number of zeroes", if you display it in the fixed-length representation, that is typically used.)
+As can be seen, the mining process doesn't compute anything special. It merely tries to find a number (also referred to as nonce) which - in combination with the payload - results in a hash with special properties.
+The advantage of using the hashcash mechanism consists of the fact, that it is very easy to check a result: Given the payload and a specific nonce, only a single call of the hashing function is needed to verify that the hash has the required properties. Since there is no known way to find these hashes other than brute force, this can be used as a "proof of work" that someone invested a lot of computing power to find the correct nonce for this payload.
+This feature is then used in the Bitcoin network to secure various aspects. An attacker that wants to introduce malicious payload data into the network, will need to do the required hashcash proof of work before it will be accepted. And as long as honest miners have more computing power, they can always outpace an attacker.
+Also see Hashcash and Proof-of-work system and SHA2 and on Wikipedia.
+ +In the early days of Bitcoin, it was easy for anyone to find new blocks using standard CPUs. As more and more people started mining, the difficulty of finding new blocks has greatly increased to the point where the average time for a CPU to find a single block can be many years. The only cost-effective method of mining is using a high-end graphics card with special software (see also Why a GPU mines faster than a CPU) and/or joining a mining pool. Since solo CPU mining is essentially useless, it was removed from the GUI of the Bitcoin software.
+ +There are two questions in here. Let's look at them separately.
+ +Mining itself is the process of creating new blocks in the block chain. Each block contains a list of all the transactions that have taken place across the entire Bitcoin network since the last block was created, as well as a hash of the previous block. New blocks are 'mined', or rather, generated, by Bitcoin clients correctly guessing sequences of characters in codes called 'hashes,' which are created using information from previous blocks. Bitcoin users may download specialized 'mining' software, which allows them to dedicate some amount of their processing power – however large or small – to guessing at strings within the hash of the previous block. Whoever makes the right guess first, thus creating a new block, receives a reward in Bitcoins.
+The block chain is one of the two structures that makes Bitcoin secure, the other being the public-key encryption system on which Bitcoin trade is based. The block chain assures that not only is every single transaction that ever takes place recorded, but that every single transaction is recorded on the computer of anyone who chooses to store the relevant information. Many, many users have complete records of every transaction in Bitcoins history readily available to them at any point, and anyone who wants in the information can obtain it with ease. These things make Bitcoin very hard to fool.
+The Bitcoin network takes considerable processing power to run, and since those with the most processing power can make the most guesses, those who put the most power toward to sustaining the network earn the most currency. Each correct guess yields, at present, fifty Bitcoins, and as Bitcoins are presently worth something (although the value still fluctuates) every miner who earns any number of Bitcoins makes money. Some miners pull in Bitcoins on their own; and some also join or form pools wherein all who contribute earn a share of the profits.
+Therefore, first answer is a vehement “yes” – no only can miners collude to get more money, Bitcoin is designed to encourage them to do so. Bitcoin pools are communal affairs, and there is nothing dishonest or underhanded about them.
+Of course, the real question is:
+ +Bitcoin isn't infallible. It can be cheated, but doing so is extremely difficult. Bitcoin was designed to evade some of the central problems with modern currencies – namely, that their trustworthiness hinges upon that of people who might not have users' best interests in mind. Every currency in the world (other than Bitcoin) is controlled by large institutions who keep track of what's done with it, and who can manipulate its value. And every other currency has value because people trust the institutions that control them.
+Bitcoin doesn't ask that its users trust any institution. Its security is based on the cryptography that is an integral part of its structure, and that is readily available for any and all to see. Instead of one entity keeping track of transactions, the entire network does, so Bitcoins are astoundingly difficult to steal, or double-spend. Bitcoins are created in a regular and predictable fashion, and by many different users, so no one can decide to make a whole lot more and lessen their value. In short, Bitcoin is designed to be inflation-proof, double-spend-proof and completely distributed.
+Nonetheless, there are a few ways that one can acquire Bitcoins dishonestly. Firstly, one can steal private keys. Key theft isn't something that Bitcoin security has been designed to prevent: it's up to users to keep theirs safe. But the cryptography is designed so that it is completely impossible to deduce someone's private key from their public one. As long as you keep your private key to yourself, you don't have much to worry about. Furthermore, one could theoretically create a new block chain, but due to the way in which the block chain is constructed, this would be extremely difficult and require massive amounts of processing power. A full explanation of the difficulties involved can be found in the block chain article.
+Bitcoin can be ripped off – but doing so would be extremely hard and require considerable expertise and a staggering amount of processing power. And it's only going to get harder with time. Bitcoin isn't impenetrable, but it's close enough to put any real worries in the peripherals.
+ +Once again, almost certainly not.
+Bitcoin is a distributed network, so any changes implemented to the system must be accepted by all users. Someone trying to change the way Bitcoins are generated would have to convince every user to download and use their software – so the only changes that would go through are those that would be equally benefit all users.
+And thus, it is more or less impossible for anyone to change the function of Bitcoin to their advantage. If users don't like the changes, they won't adopt them, whereas if users do like them, then these will help everyone equally. Of course, one can conceive of a situation where someone manages to get a change pushed through that provides them with an advantage that no one notices, but given that Bitcoin is structurally relatively simple, it is unlikely that any major changes will go through without someone noticing first.
+The fact that such changes are so difficult to make testifies to the fully distributed nature of Bitcoin. Any centrally controlled currency can be modified by its central agency without the consent of its adherents. Bitcoin has no central authority, so it changes only at the behest of the whole community. Bitcoins development represents a kind of collective evolution; the first of its kind among currencies.
+ + +
+Bitcoin Foundation standardizes, protects and promotes the use of Bitcoin cryptographic money for the benefit of users worldwide.
+OK, this is a question that often causes confusion. Here's a quick explanation! + +
As a new user, you only need to choose a wallet that you will install on your computer or on your mobile phone. Once you have your wallet installed, it will generate your first Bitcoin address and you can create more whenever you need one. You can disclose one of your Bitcoin addresses to your friends so that they can pay you or vice versa, you can pay your friends if they give you their addresses. In fact, this is pretty similar to how email works. So all that is left to do at this point is to get some bitcoins and to keep them safe. In order to start using Bitcoin, you are not required to understand the technical details.
+ +However, if you want to know more, keep reading!
+ +The blockchain is a shared public transaction log on which the entire Bitcoin network relies. All confirmed transactions are included in the blockchain with no exception. This way, new transactions can be verified to be spending bitcoins that are actually owned by the spender. The integrity and the chronological order of the blockchain are enforced with cryptography.
+ +A transaction is a transfer of value between Bitcoin addresses that gets included in the blockchain. Bitcoin wallets keep a secret piece of data called a private key for each Bitcoin address. Private keys are used to sign transactions, providing a mathematical proof that they come from the owner of the addresses. The signature also prevents the transaction from being altered by anybody once it has been issued. All transactions are broadcast between users and confirmed by the network in the following minutes, through a process called mining.
+ +Mining is a distributed consensus system that is used to confirm waiting transactions by including them in the blockchain. It enforces a chronological order in the blockchain, protects the neutrality of the network, and allows different computers to agree on the state of the system. To be confirmed, transactions must be packed in a block that fits very strict cryptographic rules that will be verified by the network. These rules prevent any previous block from being modified because doing so would invalidate all following blocks. Mining also creates the equivalent of a competitive lottery that prevents any individual from easily adding new blocks consecutively in the blockchain. This way, no individuals can control what is included in the blockchain or replace parts of the blockchain to roll back their own spends.
+ +This is only a very short and concise summary of the system. If you want to get into the details, you can read the original paper that describes the system's design, and explore the Bitcoin wiki.
diff --git a/en/img/bitcoin_at_a_glance.png b/en/img/bitcoin_at_a_glance.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..a7a9713c Binary files /dev/null and b/en/img/bitcoin_at_a_glance.png differ diff --git a/en/img/bitcoin_at_a_glance.svg b/en/img/bitcoin_at_a_glance.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..80b78bc6 --- /dev/null +++ b/en/img/bitcoin_at_a_glance.svg @@ -0,0 +1,702 @@ + + + + diff --git a/en/img/bitcoin_at_a_glance_src.svg b/en/img/bitcoin_at_a_glance_src.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..5b14f281 --- /dev/null +++ b/en/img/bitcoin_at_a_glance_src.svg @@ -0,0 +1,521 @@ + + + + diff --git a/en/index.html b/en/index.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..ef64b3d2 --- /dev/null +++ b/en/index.html @@ -0,0 +1,14 @@ +--- +layout: base-en +title: Bitcoin +--- +Bitcoin is a currency, a protocol, and a software that enables +
Bitcoin uses peer-to-peer technology to operate with no central authority: managing transactions and issuing Bitcoins are carried out collectively by the network. Through many of its unique properties, Bitcoin allows exciting uses that could not be covered by any previous payment systems.
+The software is a community-driven free open source project, released under the MIT license.
diff --git a/en/resources.html b/en/resources.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..072c9ebd --- /dev/null +++ b/en/resources.html @@ -0,0 +1,35 @@ +--- +layout: base-en +title: Resources - Bitcoin +--- +Bitcoin is a protocol that was born from a small community and has grown fast since. There are a lot of things you can do to help Bitcoin to spread and improve over time.
+ + Using Bitcoin
Using BitcoinObviously, using Bitcoin is the first thing you can do to help its development. There are most probably many cases where it can make your life easier. And you can accept payment in Bitcoin yourself.
+ + Be the network
Be the networkYou can join the Bitcoin network by keeping the original software running on your computer. You can also do some Bitcoin mining to make the network more secure by helping to process transactions.
+ + Development
DevelopmentBitcoin is open source. So if you are a developer, you can use your super-powers to do good and improve Bitcoin. Or you can also build amazing new services or software that use Bitcoin.
+ + Donation
DonationThe easiest way to help is to donate a few bitcoins or join the Bitcoin Foundation. The Foundation funds a salary for the maintainer of the core Bitcoin software, organizes conferences, and provides other important resources.
+ + Spread
SpreadSpeak about Bitcoin to interested people. Write about it on your blog. Tell your favorite shops you would like to pay with Bitcoins. Or be creative and make yourself a nice Bitcoin T-shirt.
+ + Wiki
WikiThe Bitcoin wiki is full of useful and detailed information and we are constantly improving the information it contains - just like Wikipedia. You can help keep the wiki accurate and up-to-date. + +
 Translate
TranslateBitcoin is already translated in many languages. However you can translate it in new languages as well as improving existing translations. Translations in the Bitcoin wiki would be very welcome!
+ + Help
HelpYou can join Bitcoin communities to give help to new users. And you can talk about Bitcoin with other people and learn more about it every day.
diff --git a/en/version-history.html b/en/version-history.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..e9e1c912 --- /dev/null +++ b/en/version-history.html @@ -0,0 +1,4 @@ +--- +layout: post +title: Version history +--- diff --git a/en/vocabulary.html b/en/vocabulary.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..57ab9f53 --- /dev/null +++ b/en/vocabulary.html @@ -0,0 +1,62 @@ +--- +layout: base-en +title: Vocabulary - Bitcoin +--- +Bitcoin provides a new approach to payments and as such, there are some new words that might become a part of your vocabulary. Don't worry, even the humble television created new words!
+A Bitcoin address is like a physical address or an email. It is the only information you need to provide for someone to pay you with Bitcoin.
+ +The blockchain is a public record of all Bitcoin transactions, in chronological order. The blockchain is shared between all Bitcoin users. It is used to verify the balance of Bitcoin addresses and to prevent double spending.
+ +A block is a record in the blockchain that contains and confirms many waiting transactions. Roughly every 10 minutes on average, a new block including transactions is appended to the blockchain through mining.
+ +BTC is the unofficial three letter code for Bitcoin. It can be used as an abbreviation, like USD for US dollar.
+ +Confirmation means that a transaction has been verified by the network and is highly unlikely to be reversed. One confirmation is pretty secure. Though for larger amounts ( ex. 1000 $USD and above ), one can wait for a transaction to have more confirmations - 6 is an frequently chosen number. Each new confirmation decrease the risk of a reversal exponentially.
+ +Cryptography is the branch of mathematics that lets us create mathematical proofs that provide high levels of security. Online commerce and banking already uses cryptography. In the case of Bitcoin, cryptography is used to make it impossible for anybody to spend funds from another user's wallet or to corrupt the blockchain. It can also be used to encrypt a wallet, so that it cannot be used without a password.
+ +If a malicious user tries to spend their bitcoins to two different recipients at the same time, this is double spending. Bitcoin mining and the blockchain are there to create a consensus on the network about which of the two transactions will win.
+ + +The hash rate is the measuring unit of the processing power of the Bitcoin network. The Bitcoin network must make intensive mathematical operations for security purposes. When the network reaches a hash rate of 10 TH/s, it means it can make ten trillion calculations per second.
+ +Bitcoin mining is the process of making computer hardware do mathematical calculations for the Bitcoin network to confirm transactions and increase security. As a reward for their services, Bitcoin miners can collect transaction fees for the transactions they confirm along with newly created bitcoins. Mining is a specialized and competitive market where the rewards are divided up according to how much calculation is done. Only a few Bitcoin users do Bitcoin mining and it is not an easy way to make money.
+ +Peer to peer refers to systems that work like an organized collective by allowing each individual to interact directly with the others. In the case of Bitcoin, the network is built in such a way that each user is broadcasting transactions of other users. And crucially, no bank is required as a third party.
+ +A private key is a secret piece of data that proves your right to spends Bitcoin from a specific Bitcoin address through a cryptographic signature. Each Bitcoin address has its own unique private key. Your private keys are stored in your computer if you use a software wallet while they are stored on some remote servers if you use a web wallet. Private keys must never be revealed as they allow you to spend bitcoins for their respective Bitcoin addresses.
+ +A cryptographic signature is a mathematical mechanism that allows someone to prove ownership. In the case of Bitcoin, a Bitcoin address and its private key are linked by some mathematical magic. When your Bitcoin software signs a transaction with the appropriate private key, the whole network can see that the signature matches the Bitcoin address. However, there is no way for the world to guess your private key to steal your hard-earned bitcoins.
+ +A Bitcoin wallet refers to the equivalent of a physical wallet on the Bitcoin network. Each Bitcoin wallet can show you the total balance of all Bitcoin addresses it contains. Just like you can count the money in your real wallet. And in the same way, a Bitcoin wallet allows you to pay a specific amount to a specific person. This is different to credit cards where you are charged by the merchant.
diff --git a/en/you-need-to-know.html b/en/you-need-to-know.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..6b2b7345 --- /dev/null +++ b/en/you-need-to-know.html @@ -0,0 +1,38 @@ +--- +layout: base-en +title: Some things you need to know - Bitcoin +--- +If you are about to explore Bitcoin, there are a few things you should know. Bitcoin does not let you send emails or take pictures; it lets you exchange money and value. As such, Bitcoin must be treated with the same care as your regular wallet, or even more in some cases!
+ + Securing your wallet
Securing your walletLike in real life, your wallet must be secured. Always remember that it is your responsibility to adopt good practices in order to protect your money. Here are some options you should consider.
+ +Bitcoin services and software allow you to backup your wallet, which can be printed on paper or saved to a USB drive. Stored in a safe place, a backup can protect you against computer failure and many human mistakes.
+ +Encrypting your wallet allows you to set a password for anyone trying to withdraw any funds. This helps protect against thieves and hackers, though it cannot protect against keylogging hardware or software. However, you should make sure you never forget the password or your funds will be permanently lost. Unlike your bank, there are no password recovery options with Bitcoin!
+ +Using a online wallet is pretty much like using a online bank. You are trusting someone else to protect your money while you have to remember and protect your password. Your should always choose such services carefully. As of today, no online wallet provides enough insurance and security to be used to store value like a bank.
+ +An offline backup of a wallet provides the highest level of security for savings. It involves storing a wallet only on paper and on usb keys in different secured locations that are not connected to the network. This is a good protection against computer failures, computer vulnerabilities, theft and human mistakes. As of today, this approach still requires some technical knowledge to be done correctly.
+ Bitcoin value is volatile
Bitcoin value is volatileThe value of Bitcoin can unpredictably increase or decrease over a short period of time due to its young economy, novel nature, and sometimes-illiquid markets. Consequently, keeping your savings in Bitcoin is not recommended. Bitcoin should be considered as a high risk asset and you should never store money that you cannot afford to lose with Bitcoin. If you receive payments with Bitcoin, many service providers allow you to convert them instantly to your local currency.
+ + Bitcoin payments are irreversible
Bitcoin payments are irreversibleAny transaction you issue with Bitcoin cannot be reversed. It can only be refunded by the person receiving the funds. That means you should take care to do business with people or organizations you know and trust. But don't worry, Bitcoin can detect typos and usually won't let you send money to an invalid address.
+ + Bitcoin is not anonymous without efforts
Bitcoin is not anonymous without effortsAll Bitcoin transactions are stored publicly and permanently on the network, which means anybody can see the balance and the transactions of any Bitcoin address. However, it is not possible to associate a Bitcoin address with its physical owner unless the owner demonstrated that they own it. This is why it is recommended to use many different Bitcoin addresses; in fact, you should create a new one each time you receive money. This is especially important for public uses such as websites. You might also want to consider hiding your computer's IP address with a tool like Tor so that it cannot be logged by others.
+ + Bitcoin is still experimental
Bitcoin is still experimentalBitcoin is an experimental new currency that is in active development. Although it becomes less and less experimental as usage grows, you should keep in mind that Bitcoin is a new invention that is exploring ideas that have never been attempted before. As such, its future cannot be predicted by anyone.
+ + Don't forget to pay your taxes
Don't forget to pay your taxesBitcoin is not a official currency. That said, most jurisdictions still require you to pay income, sales, and payroll taxes on anything that has value, including Bitcoin. It is your responsibility to inform yourself about and comply with any applicable laws.
diff --git a/favicon.ico b/favicon.ico index d249e41f..2534bce7 100644 Binary files a/favicon.ico and b/favicon.ico differ diff --git a/favicon.png b/favicon.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..75c1c97f Binary files /dev/null and b/favicon.png differ diff --git a/feb20.html b/feb20.html index db1dfe7f..6cb4acc5 100644 --- a/feb20.html +++ b/feb20.html @@ -1,5 +1,5 @@ --- -layout: simple +layout: base-en ---Bitcoin est une des premières implémentation d'un concept appelé crypto-devise, initialement décrit en 1998 par Wei Dai sur la liste de diffusion the cypherpunks. En se basant sur la notion que la monnaie peut être n'importe quel objet, ou toute forme de registre, acceptée sous forme de paiement pour des biens et des services et le paiement d'une dette dans un contexte étatique ou socio-économique, le Bitcoin a été conçu avec l'idée de créer une nouvelle forme de monnaie qui utilise la cryptographie pour contrôler sa création monétaire et ses transactions, plutôt que de dépendre d'une autorité centrale.
+En 2009, la première spécification et la première preuve de concept du Bitcoin est publiée dans la liste de diffusion Cryptography par un membre sour le pseudonyme de Satoshi Nakamoto. Vers la fin de l'année 2010, Satoshi délaisse le projet. De tout ce temps, le créateur du Bitcoin n'a jamais révélé son identité et a laissé son invention au public. L'origine et la motivation derrière la création du Bitcoin sont encore aujourd'hui une grande source de mystère.
+Depuis 2010, la communauté Bitcoin gagne une forte croissance avec plusieurs développeurs bénévoles impliqués dans le projet. Au cours de juin et juillet 2011, le Bitcoin reçoit soudainement l'attention des médias, créant une bulle spéculative massive qui s'essoufle ensuite rapidement. La valeur du Bitcoin grimpe ensuite progressivement jusqu'à rejoindre sa montée spectaculaire de 2011.
+Le 27 septembre 2012, la Bitcoin foundation est créée afin de standardiser, protéger et promouvoir le Bitcoin. Et à ce jour, l'économie du Bitcoin est en forte croissance.
+ +Voici les propriétés de base de tout réseau reposant sur un protocole basé sur Bitcoin.
+Ces règles sont imposées collectivement par le réseau. Bien qu'elles ne changeront pas pour le Bitcoin, d'autres monnaies virtuelles utilisant la technologie du Bitcoin peuvent les changer pour s'adapter à leurs besoins.
+Le réseau fonctionne depuis plus de 45 mois, donnant lieu à des caractéristiques de sécurité impressionnantes. Et une croissance significative au cours de la dernière année. Au cours de février 2013, voici quelques statistiques.
+Le Bitcoin peut propulser des systèmes innovants, ou les plus habituels.
+ + La plus simple des configurations de paiement
La plus simple des configurations de paiementÀ moins que les paiements doivent être associés une facturation automatisée, accepter les Bitcoin est aussi simple que d'ajouter une adresse Bitcoin sur un site web sous forme de texte ou sous la forme d'une image représentant le code QR. Cette approche simple est à la portée de tous et peut répondre des besoins d'une bonne palette de clients. Spécialement pour les dons.
+ + Plusieurs APIs de programmation
Plusieurs APIs de programmationIl existe de nombreux services de traitement de paiement qui offrent des APIs de programmation. De telle sorte que vous ne soyez pas obligés de conserver de Bitcoins sur votre serveur ni prendre en charge la sécurité que cela implique. Du même coup, la plupart de ces APIs vous permettent d'échanger vos Bitcoin contre votre propre devise locale à des prix compétitifs.
+ + Devenez votre propre système financier
Devenez votre propre système financierSi vous n'utilisez pas d'API de programmation offert par un tiers, vous pouvez intégrer un serveur Bitcoin directement dans vos applications. Vous permettant ainsi de devenir votre propre banque et de traiter vous-même tous vos paiements. Avec toutes les responsabilités que cela implique, vous pouvez construire des systèmes autonomes utilisant le Bitcoin pratiquement sans le moindre frais.
+ + Les adresses Bitcoin pour associer une facture
Les adresses Bitcoin pour associer une factureBitcoin peut virtuellement créer autant d'adresse Bitcoin qu'un utilisateur le désire. Ce qui signifie que si vous souhaitez développer un système de paiement associé à un numéro de facture, vous avez simplement besoin de générer et surveiller une adresse Bitcoin pour chaque paiement. Vous pouvez aussi ré-utiliser les même adresses une fois les paiements complétés.
+ + Presque toute la sécurité est du côté du client
Presque toute la sécurité est du côté du clientLa plus grande partie de la sécurité s'effectue par le biais du protocole du côté du client et du côté du réseau Bitcoin. L'authenticité des payeurs est vérifiée grâce aux clés privées et la double-dépense est bloquée par le réseau Bitcoin. Ce qui signifie que vous n'avez pas à vous soucier d'être conforme avec la norme PCI ou d'implémenter des détections de fraudes. Bitcoin fonctionne, point à la ligne.
+ + Transactions instantanées et confirmations
Transactions instantanées et confirmationsUne transaction Bitcoin est normalement déployée à l'intérieur de quelques secondes et confirmée dans les 10 minutes suivantes. Avant quoi, la transaction peut être considérée comme authentique mais réversible. Si vous avez réellement besoin d'utiliser les transactions instantanées, il est recommandé d'exiger un petit frais de transaction et d'utiliser un système de détection des doubles-dépenses.
+ + Les micro paiements accessibles
Les micro paiements accessiblesBitcoin offre les frais de transaction les plus bas pour tout type de paiement, incluant les micro-paiements. Ce qui signifie qu'il peut aussi être utilisé pour concevoir et implémenter des nouveaux services en ligne créatifs qui ne pouvaient pas exister pour de simples restrictions financières.
diff --git a/fr/bitcoin-pour-organisations.html b/fr/bitcoin-pour-organisations.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..e8834636 --- /dev/null +++ b/fr/bitcoin-pour-organisations.html @@ -0,0 +1,30 @@ +--- +layout: base-fr +title: Bitcoin pour les Entreprises - Bitcoin +--- +Bitcoin est un moyen très sécuritaire et économique de traiter des paiements.
+ + Les frais les plus compétitifs
Les frais les plus compétitifsLa haute sécurité cryptographique du Bitcoin lui permet de traiter des transactions de manière extrêmement efficace et économique. À ce jour, vous pouvez émettre et recevoir des paiements gratuitement en utilisant le réseau Bitcoin dans la plupart des cas. Et vous pouvez payer un petit frais de transaction volontaire si vous voulez augmenter la priorité d'une de vos transactions.
+ + Protection contre les fraudes par renversement
Protection contre les fraudes par renversementToutes les entreprises qui acceptent les paiements par cartes de crédit ou Paypal connaissent le problème que représente les paiements qui sont plus tard renversés lorsque le compte du payeur a été piraté ou lorsque le payeur prétend frauduleusement ne pas avoir reçu son achat. Les entreprises ne peuvent pas se défendre contre ce type de fraude, hormis par des analyses de risque complexes et en augmentant leurs prix pour couvrir les pertes. Les paiements Bitcoin sont irréversibles. Ce qui signifie que les coûts de la fraude ne sont plus poussés sur les épaules des marchands.
+ + Transferts internationaux sans délais
Transferts internationaux sans délaisLes Bitcoins peuvent être transférés de l'Afrique vers le Canada en 10 minutes. En fait, les Bitcoins n'ont aucun emplacement géographique fixe. Ce qui signifie que vous pouvez transférer n'importe quelle somme vers n'importe quelle destination sans limite, sans délais et sans frais excessifs. Il n'y a pas de banque intermédiaire pour ralentir vos paiement pendant 3 jours ouvrables.
+ + Aucune conformité PCI requise
Aucune conformité PCI requiseAccepter les cartes de crédit en ligne requiert une liste exhaustive de vérifications et de formalités toujours renouvellées afin de se conformer à la norme PCI. Bien que ce soit une bonne chose pour protéger les cartes de crédit, la sécurité du Bitcoin est pour sa part conçue de manière à rendre cette approche désuète. Vos paiements sont sécurisés par le réseau. Pas aux frais de votre entreprise.
+ + Transactions instantanées pour les points de vente
Transactions instantanées pour les points de venteUne transaction Bitcoin est normalement déployée en quelques secondes et confirmée en 10 minutes. Avant quoi, cette transaction peut être considérée comme authentique mais réversible. Si vous avez vraiment besoin d'utiliser les transactions instantanées, il est recommandé d'exiger un léger frais de transaction et d'utiliser un système de détection des doubles-dépenses.
+ + Gagner de la visibilité avec peu d'effort
Gagner de la visibilité avec peu d'effortLe Bitcoin est un marché émergeant où de nouveaux consommateurs sont à la recherche de biens et de services en échange de leurs Bitcoins. Les accepter est une bonne façon d'obtenir de nouveaux clients et de donner à votre entreprise un peu plus de visibilité. Accepter de nouvelles formes de paiements est une pratique futée depuis longtemps réputée pour les commerces en ligne.
+ + Multi-signature
Multi-signatureBitcoin inclut également une fonctionnalité encore peu connue permettant d'empêcher la dépense de certains Bitcoins à moins qu'un nombre défini d'un groupe de personnes ne signe la transaction. C'est ce qu'on appelle souvent les transactions "n de m". Ce système représente l'équivalent du bon vieux chèque à signatures multiples que vous utilisez peut-être encore aujourd'hui.
+ + Transparence dans votre comptabilité
Transparence dans votre comptabilitéPlusieurs organisations sont tenues de produire des documents sur leurs activités et d'adopter de bonnes pratiques de transparence. Utiliser le Bitcoin offre le plus haut niveau de transparence puisque vos soldes et chacune de vos transactions peut être consultée en ligne par chacun de vos membres que vous tenez au courant de vos adresses Bitcoin.
diff --git a/fr/bitcoin-pour-particuliers.html b/fr/bitcoin-pour-particuliers.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..befd6ee8 --- /dev/null +++ b/fr/bitcoin-pour-particuliers.html @@ -0,0 +1,24 @@ +--- +layout: base-fr +title: Bitcoin pour les Particuliers - Bitcoin +--- +Bitcoin est la manière la plus simple et économique d'échanger de l'argent.
+ + Paiements mobiles simplifiés
Paiements mobiles simplifiésBitcoin sur les mobiles vous permet de payer avec la meilleure simplicité avec un simple scan. Aucun besoin de passer votre carte, de taper un code NIP ou de signer. Tout ce que vous devez faire pour recevoir des paiements Bitcoin est d'afficher le code QR avec votre application Bitcoin et de laisser un ami scanner votre mobile, ou de mettre en contact les deux mobiles ( avec la technologie NFC ).
+ + Transferts internationaux sans délais
Transferts internationaux sans délaisLes Bitcoins peuvent être transférés de l'Afrique vers le Canada en 10 minutes. Il n'y a aucune banque pour ralentir le traitement de vos transations, engoutir des frais substantiels ou même geler votre tranfert. Vous pouvez payer votre voisin exactement de la même façon que vous pouvez payer un membre de votre famille dans un autre pays.
+ + Fonctionne partout, en tout temps
Fonctionne partout, en tout tempsTout comme les emails, vous n'avez pas besoin de forcer qui que ce soit à utiliser le même logiciel ou la même banque que vous. Laissez à vos amis et à votre famille le libre choix de leur service favoris. Aucun problème, tous les services Bitcoins sont compatibles entre eux puisqu'ils utilisent la même technologie ouverte. Le réseau Bitcoin ne dors jamais, même le dimanche!
+ + Transactions sécurisées
Transactions sécuriséesLes transactions Bitcoin sont sécurisées par une cryptographie de niveau militaire. Personne ne peut faire de paiement en votre nom ou vous charger une somme sans avoir une copie de votre porte-monnaie. Tant que vous faites le nécessaire pour protéger votre porte-monnaie, Bitcoin offre un niveau de protection intéressante contre plusieurs formes de fraudes.
+ + Presque 100% gratuit
Presque 100% gratuitVous pouvez déjà envoyer et recevoir des paiements gratuitement! À l'exception de cas spéciaux comme les très petits paiements, il n'y a aucun frais obligatoire. Vous pouvez toutefois décider volontairement de verser un frais de transaction pour augmenter la priorité de traitement de votre paiement. Et ainsi rémunérer du même coup les personnes qui font fonctionner le réseau Bitcoin.
+ + Paiements en ligne anonymes
Paiements en ligne anonymesLes paiements anonymes font partie de notre vie de tous les jours. La plupart des achats faits en boutique sont complétés sans obligation s'identifier. Bitcoin introduit la même liberté dans le monde du web. Vous permettant d'acheter des services ou de faire des dons sans le désagrément d'être passé au rayon X. Toutefois, vous devez savoir que l'anonymat complet requiert des efforts spéciaux.
diff --git a/fr/bitcoin-pour-passionnes.html b/fr/bitcoin-pour-passionnes.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..1da19062 --- /dev/null +++ b/fr/bitcoin-pour-passionnes.html @@ -0,0 +1,29 @@ +--- +layout: base-fr +title: Bitcoin pour les Passionnés +--- +Bitcoin change le monde des finances en le rendant plus ouvert et démocratique.
+ + Bitcoin est un consensus mondial et démocratique
Bitcoin est un consensus mondial et démocratiqueDe par sa nature libre et décentralisée, Bitcoin est le premier réseau de paiement qui fonctionne uniquement grâce à ses utilisateurs et sans autorité centrale. Même les développeurs du Bitcoin n'ont aucun pouvoir de forcer une mise à jour dans le protocole si suffisamment d'utilisateurs, de développeurs ou de mineurs sont en désaccord. Vous seul avez le contrôle exclusif de votre porte-monnaie.
+ + Une monnaie conçue pour Internet
Une monnaie conçue pour InternetBitcoin est né de l'Internet. Introduisant à son passage les libertés de la monnaie physique dans le monde du web tout en rendant les paiements plus faciles et sécuritaires dans les deux mondes. Bitcoin peut offrir des alternatives concrètes à plusieurs systèmes anciens, lourds et couteux. Et il peut augmenter l'accessibilité du commerce en ligne dans les pays en voie de développement.
+ + Protéger les droits et libertés individuelles
Protéger les droits et libertés individuellesBitcoin permet à chaque personne de stocker et échanger de la valeur sécuritairement sur un réseau qui ne peut être saisi, manipulé ou stoppé par aucune organisation ou individu. Donnant ainsi un libre accès à des outils puissants qui peuvent jouer un rôle dans la protection des droits et libertés individuelles contre plusieurs niveaux de corruption.
+ + La première devise globale et neutre
La première devise globale et neutreOn ne peut que difficilement trouver une monnaie dans notre histoire qui ait déjà été libre de toute influence politique ou de toute économie nationale. Le Bitcoin pourrait-il devenir la première devise globale à traverser toutes les barrières entre les nations, les politiques et les cultures pour le bénéfice du bien commun? Tout ça semble possible. Un pour tous, et tous pour un!
+ + Promouvoir la transparence
Promouvoir la transparenceToutes les transactions Bitcoin sont publiques. Mais les propriétaires et les destinataires de ces transactions restent inconnus. Les organisations peuvent choisir de révéler leur propriété sur certaines adresses Bitcoins envers des personnes définies. Ce qui permet à toute organisation de mettre en oeuvre d'excellentes pratiques de transparence adaptées à chaque besoin. +
+ + Rendre l'argent plus sécuritaire
Rendre l'argent plus sécuritaireGrâce à un usage ingénieux de règles cryptographiques, le Bitcoin offre une liste étonnante de fonctionnalités reliées à la sécurité. Non seulement les Bitcoins sont impossibles à contrefaire ou à usurper mais le protocole est aussi conçu pour être très résistant contre une liste impressionnante d'attaques informatiques, incluant les attaques par déni de service distribué. +
+ + Résoudre les problèmes de confiance des banques
Résoudre les problèmes de confiance des banquesBitcoin offre des solutions contre plusieurs problèmes de confiance entre les banques avec la transparence comptable sélective, les preuves par signature cryptographiques et les transactions irréversibles. Bitcoin augmente aussi les risques des banques malhonnêtes. Aucun nouveau Bitcoin ne peut être créé pour les sauver de leurs propres erreurs aux frais des citoyens.
diff --git a/fr/choisir-votre-porte-monnaie.html b/fr/choisir-votre-porte-monnaie.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..fe484e5a --- /dev/null +++ b/fr/choisir-votre-porte-monnaie.html @@ -0,0 +1,106 @@ +--- +layout: base-fr +title: Choisir votre porte-monnaie - Bitcoin +--- + + + +Votre porte-monnaie Bitcoin est ce qui vous permet de faire des transactions avec le monde. Il vous rend propriétaire de quelques adresses Bitcoin que vous pouvez utiliser pour recevoir et envoyer des Bitcoins avec d'autres utilisateurs. Et comme les emails, vous pouvez recevoir des Bitcoins lorsque vous êtes hors-ligne et tous les porte-monnaies Bitcoin sont compatibles entre eux.
+Si vous êtes un nouvel utilisateur, ces porte-monnaie sont un bon point de départ.
+Possédez-vous un ordinateur que vous gardez ouvert en permanence? Vous pouvez aider la communauté simplement en laissant fonctionner le logiciel Bitcoin original sur celui-ci. Le logiciel Bitcoin original est exigeant en ressource and prendra plus d'une journée entière pour se synchroniser. Après quoi, votre ordinateur contribuera au réseau en partageant les transactions et la chaîne de bloc.
 Porte-monnaie logiciel
Porte-monnaie logicielLes porte-monnaie logiciels sont installés dans votre ordinateur. Ceux-ci vous donnent un contrôle complet sur vos Bitcoins. Vous êtes responsables de faire des sauvegardes et de le protéger. De la même manière que l'argent liquide.
+ + +


Bitcoin-Qt est le logiciel Bitcoin original sur lequel s'appuie le réseau. Il offre le plus haut niveau de sécurité, de vie privée et de stabilité. Toutefois, il offre moins de fonctionnalités et prend beaucoup d'espace et de mémoire.
+ + + +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ 


Multibit est un client léger qui se concentre à être rapide et facile d'usage. Il se synchronise avec le réseau et est prêt en quelques minutes. Multibit supporte aussi plusieurs languages. Il est un bon choix pour les novices.
+ + + +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ 

Armory est un client Bitcoin avancé qui élargit les fonctionnalités de Bitcoin-Qt pour les super-utilisateurs. Armory offre plusieurs formes de sauvegardes et d'encryption et il permet une utilisation hors-ligne sécurisée.
+ + + +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ 



Electrum se spécialise dans la rapidité et la simplicité. Electrum est très léger et utilise des serveurs distants pour augmenter ses performances. Il conserve aussi une sauvegarde encryptée en ligne de votre porte-monnaie.
+ + + +
+
+
+ Porte-monnaie mobile
Porte-monnaie mobileLes porte-monnaie mobiles vous permettent d'apporter le Bitcoin avec vous. Vous pouvez échanger des Bitcoins de personne à personne et payer dans des boutiques par un simple scan du code QR affiché sur un écran, ou avec NFC.
+ + +
Bitcoin Wallet est un client mobile léger qui est disponible pour les mobiles et tablettes Android. Cette application n'a pas besoin d'être associée à un service en ligne. Et il est compatible avec le scan de codes QR et la technologie NFC.
+ + + +
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ 

Blockchain est un porte-monnaie mobile qui fonctionne avec le service en ligne blockchain.info. Il est disponible pour iPhones dans une version compatible avec les restrictions d'Apple et il inclut les options de blockchain.info .
+ + + +
+
+
+ Porte-monnaie en ligne
Porte-monnaie en ligneLes porte-monnaie en ligne vous permettent d'utiliser vos Bitcoins partout avec moins à faire pour les protéger. Toutefois, vous devez choisir un porte-monnaie en ligne avec prudence puisque ces services hébergent vos Bitcoins.
+ + +Est un porte-monnaie en ligne très simple. Le service conserve une version encryptée de votre porte-monnaie mais le décryptage se passe dans votre navigateur. Par sécurité, utilisez l'extension et les emails de sauvegarde.
+ + + +
+
+
+Voici une question à problème. Essayons une explication rapide! + +
Comme nouvel utilisateur, vous avez seulement besoin de choisir un porte-monnaie que vous installerez sur votre ordinateur ou sur votre mobile. Une fois prêt, votre porte-monnaie créera votre première adresse Bitcoin et vous pouvez en créer de nouvelles chaque fois que vous en avez besoin. Vous pouvez communiquer l'une de vos adresses Bitcoin à un ami pour qu'il puisse vous payer. De la même façon, vous pouvez payer vos amis s'ils vous donnent leurs adresses. En fait, échanger des Bitcoins est assez similaire à échanger des emails. Ensuite, il ne reste qu'à obtenir quelques Bitcoins et à les garder en sûreté. En tant qu'utilisateur, vous n'avez pas besoin de connaître le fonctionnement technique.
+ +Toutefois, si vous voulez en savoir plus, continuez votre lecture!
+ +La chaîne de bloc est un journal de transactions partagé et public sur lequel repose le réseau Bitcoin. Toutes les transactions confirmées sont incluses dans la chaîne de blocs sans exception. De cette façon, il est possible de vérifier que chaque nouvelle transaction échange des bitcoins appartenant à l'émetteur du paiement. L'intégrité et l'ordre chronologique de la chaîne de bloc est protégée par la cryptographie.
+ +Une transaction est un transfert de valeur entre des adresses Bitcoin qui est incluse dans la chaîne de bloc. Les porte-monnaie Bitcoin conservent une information secrète pour chaque adresse Bitcoin qu'on appelle clé privée. Les clés privées sont utilisées pour signer chaque transaction, fournissant une preuve mathématique qu'elles proviennent des bons propriétaires. La signature permet également d'empêcher la transaction d'être modifiée une fois émise. Toutes les transactions sont diffusées entre les utilisateurs et sont confirmées par le réseau dans les minutes suivantes via un procédé nommé minage.
+ +Le minage est un système de consensus distribué qui est utilisé pour confirmer les transactions en attente en les incluant dans la chaîne de bloc. Le minage impose un ordre chronologique dans la chaîne de bloc, protège la neutralité du réseau et permet aux ordinateurs du réseau d'être en accord sur l'état du système. Pour être confirmées, les transactions doivent être incluses dans un bloc qui doit correspondre à des règles cryptographiques très strictes qui sont ensuite vérifiées par le réseau. Ces règles empêchent la modification d'un bloc antérieur car la logique des blocs suivants serait brisée. Et elles créent l'équivalent d'une loterie compétitive qui empêche tout individu d'ajouter des blocs consécutivement dans la chaîne de bloc. De cette façon, aucun individu ne peut contrôler ce qui est inclut dans la chaîne de bloc ni en remplacer des parties pour annuler ses propres transactions.
+ +Tout cela n'est qu'un résumé très court et concis du système. Si vous voulez aller plus loin dans les détails, vous pouvez lire la spécification originale ou explorer le Wiki Bitcoin.
diff --git a/fr/communaute.html b/fr/communaute.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..3c6179e3 --- /dev/null +++ b/fr/communaute.html @@ -0,0 +1,22 @@ +--- +layout: base-fr +title: Communauté - Bitcoin +--- +Si vous êtes intéressés à en apprendre davantage sur les détails techniques du Bitcoin, il est recommandé de commencer avec ces documents.
+ + +Le développement du Bitcoin est ouvert et tout développeur peut contribuer au projet. Tout ce que vous devez savoir est dans le dépôt Github. Veuillez vous assurer de lire et de suivre le processus de développement décrit dans le README ainsi que de produire du code de qualité.
+ +Classé par le nombre d'ajouts dans le code
+|
+ {% if c.gravatar_id %}
+ |
+ {% cycle nil, nil, nil, nil, '
 +
+La Fondation Bitcoin standardise, protège et promouvoit l'utilisation de la monnaie cryptographique Bitcoin pour le bénéfice de ses utilisateurs mondiaux.
+Bitcoin est une devise, un protocole et un logiciel qui rend possible : +
Bitcoin utilise une technologie pair à pair pour fonctionner sans autorité centrale. Le traitement des transactions et la création des Bitcoins est prise en charge collectivement par le réseau. Par le biais de ses propriétés uniques, le Bitcoin rend possible des usages prometteurs qui ne pouvaient pas être couverts par les systèmes de paiement précédents.
+Le logiciel Bitcoin est un logiciel libre développé par la communauté et publié sous la licence MIT.
diff --git a/fr/ressources.html b/fr/ressources.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..431677f7 --- /dev/null +++ b/fr/ressources.html @@ -0,0 +1,35 @@ +--- +layout: base-fr +title: Ressources - Bitcoin +--- +Le Bitcoin est un protocole né d'une petite communauté et qui a grandi rapidement. Il y a beaucoup de choses que vous pouvez faire pour aider le Bitcoin à se propager et à s'améliorer.
+ + Utiliser Bitcoin
Utiliser BitcoinBien entendu, utiliser Bitcoin est la première chose que vous pouvez faire pour aider son développement. Il y a probablement plusieurs cas où il peut déjà vous rendre la vie plus facile. Et vous pouvez vous-même accepter d'être payé avec les Bitcoin.
+ + Devenir le réseau
Devenir le réseauVous pouvez faire partie du réseau Bitcoin en laissant le logiciel Bitcoin original fonctionner en permanence sur votre ordinateur. Et vous pouvez faire du minage de Bitcoin pour aider le réseau à devenir toujours plus sécuritaire en plus d'aider le traitement des transactions.
+ + Développement
DéveloppementLe code source du Bitcoin est ouvert. Donc si vous êtes un développeur, vous pouvez utiliser vos super pouvoirs pour faire le bien et améliorer Bitcoin. Mais vous pouvez aussi construire des services ou des logiciels fantastiques qui fonctioneront avec le Bitcoin.
+ + Dons
DonsLa manière la plus facile d'aider Bitcoin est de faire un don de quelques Bitcoins ou de rejoindre la fondation Bitcoin. La fondation offre un salaire aux développeurs qui font fonctionner le coeur du réseau Bitcoin, elle organise des conférences et elle fournit d'autres ressources importantes.
+ + Propager
PropagerParler du Bitcoin à des personnes intéressées. Écrivez à propos du Bitcoin dans votre blog. Dîtes à votre boutique favorite que vous aimeriez pouvoir payer en Bitcoin. Ou soyez créatifs et faîtes-vous imprimer un superbe t-shirt sur le Bitcoin.
+ + Wiki
WikiLe Wiki Bitcoin contient un nombre impressionnant d'informations détaillées. Et le wiki est en constante recherche d'amélioration de la même manière que Wikipedia. Vous pouvez aider à maintenir le wiki à jour et veiller à protéger l'exactitude de chaque information présentée.
+ + Traduction
TraductionLe logiciel Bitcoin original est déjà traduit dans plusieurs langues. Toutefois, vous pouvez le traduire dans de nouvelles langues ainsi que vérifier si vous pouvez améliorer les traductions existantes. Plus de traductions dans le Wiki Bitcoin serait aussi largement apprécié!
+ + Aide
AideVous pouvez rejoindre les communautés Bitcoin pour aider et assister les nouveaux utilisateurs. Et vous pouvez discuter à propos du Bitcoin avec d'autres utilisateurs et en apprendre plus à chaque jour.
diff --git a/fr/telecharger.html b/fr/telecharger.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..25aaee59 --- /dev/null +++ b/fr/telecharger.html @@ -0,0 +1,15 @@ +--- +layout: base-fr +title: Télécharger - Bitcoin +--- +
+ Télécharger pour Windows (zip) ~13MB
Télécharger pour Windows (zip) ~13MB
+ Télécharger pour Windows (exe) ~9MB
Télécharger pour Windows (exe) ~9MB
+ Télécharger pour Ubuntu (PPA)
Télécharger pour Ubuntu (PPA)
+ Télécharger pour Linux (tgz, 32/64-bit) ~12MB
Télécharger pour Linux (tgz, 32/64-bit) ~12MB
+ Télécharger pour Mac OS X ~13MB
Télécharger pour Mac OS X ~13MB
+ Code source (GitHub)
+ Voir l'historique des versions (anglais)
+
Bitcoin offre une nouvelle approche avec les paiements. De fait, certains mots nouveaux pourraient entrer dans votre dictionnaire. Ne vous en faites pas, même la radio a un jour créé de nouveaux mots.
+Une adresse Bitcoin est comme une adresse physique ou une adresse email. Il s'agit de la seule information que vous avez besoin de fournir pour qu'une personne vous paie avec des Bitcoins.
+ +La chaîne de bloc est un journal public de toutes les transactions Bitcoin, en ordre chronologique. Celle-ci est partagée entre tous les utilisateurs du réseau Bitcoin. Et elle est utilisée pour vérifier le solde des adresses Bitcoin et pour empêcher la double dépense.
+ +Un bloc est un ajout dans la chaîne de bloc qui contient et confirme plusieurs transactions en attente. Environ chaque 10 minutes, un bloc est ajouté à la chaîne de bloc via le minage.
+ +BTC est le code ISO non officiel pour le Bitcoin. Il peut être utilisé comme une abbréviation, de la même façon que USD pour le dollar américain.
+ +Une confirmation signifie qu'une transaction a été vérifiée par le réseau et que ses chances d'être renversée sont quasi inexistantes. Une seule confirmation offre un bon niveau de sécurité. Quoi que pour les paiements importants ( ex. 1000 $USD et plus ), vous pouvez attendre qu'une transaction ait accumulé davantage de confirmations - 6 confirmations est la norme la plus courante. Chaque nouvelle confirmation diminue le risque d'un renversement de façon exponentielle.
+ +La cryptographie est une branche de la mathématique permettant de créer des preuves mathématiques qui offrent un haut niveau de sécurité. De nos jours, tout commerce ou banque en ligne utilise déjà la cryptographie. Avec le Bitcoin, la cryptographie est utilisée pour empêcher quiconque de dépenser les fonds d'un autre utilisateur et pour empêcher la corruption de la chaîne de bloc. Elle peut aussi être utilisée pour encrypter un porte-monnaie, afin qu'il ne puisse être utilisé qu'avec un mot de passe.
+ +Si un utilisateur mal intentionné essaie de dépenser ses Bitcoins envers deux destinataires au même moment, il s'agit de double dépense. Le minage et la chaîne de bloc existent pour créer un consensus afin de décider laquelle des deux transactions sera confirmée.
+ +Le taux de hash est l'unité de mesure de la puissance de calcul du réseau Bitcoin. Le réseau Bitcoin doit faire des calculs mathématiques intensifs pour des raisons de sécurité. Quand le réseau atteint un taux de hash de 10 TH/s, cela signifie qu'il peut faire dix billions de calculs par seconde.
+ +Le minage de Bitcoin est le procédé d'utiliser du matériel informatique pour effectuer des calculs mathématiques pour le réseau Bitcoin afin de confirmer des transactions et augmenter la sécurité. Comme récompense pour leurs services, les mineurs de Bitcoin collectent les frais de transaction pour les transactions qu'ils confirment et les Bitcoins nouvellement créés. Le minage est un marché compétitif où les revenus sont divisés en fonction du nombre de calculs effectués. Seulement une petit fraction des utilisateurs du Bitcoin font du minage et il ne s'agit pas d'un moyen facile de gagner de l'argent.
+ +Pair à pair réfère à une forme de système qui fonctionne comme une collectivité organisée. Permettant à chaque individu d'interagir directement avec les autres. Dans le cas du Bitcoin, le réseau est construit de manière à ce que chaque utilisateur diffuse les transactions des autres utilisateurs. Et aucune banque n'est requise en tant que tiers entre les utilisateurs.
+ +Une clé privée est une information secrète qui permet de prouver votre droit de dépenser des bitcoins à partir d'une adresse Bitcoin définie grâce à une signature cryptographique. Chaque adresse Bitcoin a sa propre clé privée unique. Vos clés privées sont stockées dans votre ordinateur si vous utilisez un porte-monnaie logiciel tandis qu'elles sont stockés sur des serveurs en ligne si vous utilisez un porte-monnaie en ligne. Les clés privées ne doivent jamais être révélées car elles permettent de dépenser les bitcoins des adresses Bitcoin auxquelles elles sont associées.
+ +Une signature cryptographique est un mécanisme mathématique qui permet de prouver son authenticité. Dans le cas du Bitcoin, une adresse Bitcoin et sa clé privée sont liés par la magie de la mathématique. Quand un logiciel Bitcoin signe une transaction avec la clé privée appropriée, le réseau Bitcoin peut vérifier que la signature correspond à l'adresse Bitcoin dans la transaction. Malgré tout, il n'existe aucun moyen de deviner quelle est la clé privée afin de voler des bitcoins durement gagnés.
+ +Un porte-monnaie Bitcoin réfère à l'équivalent d'un porte-monnaie physique sur le réseau Bitcoin. Chaque porte-monnaie peut afficher le solde des adresses Bitcoin qu'il contient. De la même façon que vous pouvez compter l'argent dans votre porte-monnaie. Un porte-monnaie Bitcoin partage aussi la similarité de vous permettre de payer un montant spécifique à une personne spécifique. À l'inverse des cartes de crédit où vous êtes chargés par le marchand.
diff --git a/fr/vous-devez-savoir.html b/fr/vous-devez-savoir.html new file mode 100644 index 00000000..2d100732 --- /dev/null +++ b/fr/vous-devez-savoir.html @@ -0,0 +1,35 @@ +--- +layout: base-fr +title: Ce que vous devez savoir - Bitcoin +--- +Si vous êtes sur le point d'explorer le Bitcoin, il y a certaines choses que vous devez savoir. Bitcoin ne sert pas à échanger des emails ou des images. Il vous permet d'échanger de l'argent et de la valeur. De fait, Bitcoin doit recevoir la même prudence de votre part que votre porte-monnaie.. Voir parfois plus!
+ + Sécuriser votre porte-monnaie
Sécuriser votre porte-monnaieComme votre argent liquide, votre porte-monnaie doit être protégé. Rappelez-vous que vous êtes responsables d'adopter des pratiques pour protéger votre argent. Voici quelques options à considérer.
+ +Les services et logiciels Bitcoin vous permettent de sauvegarder votre porte-monnaie ou vos clés privées. Qui peuvent être imprimées sur du papier ou sauvegardées sur une clé USB. Stockés dans un endroit sécuritaire, une sauvegarde peut vous protéger contre des pannes informatiques ou diverses erreurs humaines.
+Encrypter votre porte-monnaie vous permet d'appliquer un mot de passe contre quiconque tenterait de retirer des fonds. Ce qui peut vous protéger contre le vol et le piratage. Mais pas contre les enregistreurs de frappe. Vous devez vous assurer de ne jamais oublier votre mot de passe sinon votre argent sera perdu. Contrairement à votre banque, vous ne pouvez pas récupérer votre mot de passe avec Bitcoin!
+Utiliser un porte-monnaie en ligne est un peu comme utiliser une banque en ligne. Vous accordez votre confiance à une entreprise pour stocker votre argent tandis qu'il ne vous reste qu'à vous souvenir de votre mot de passe et à le protéger. Vous devez choisir ce genre de service avec prudence. À ce jour, aucun de ces services n'offre assez d'assurance et de sécurité pour stocker de la valeur comme une banque.
+Utiliser un porte-monnaie hors-ligne offre le plus haut niveau de sécurité pour l'épargne. Il implique de stocker un porte-monnaie seulement sur papier et sur des clés usb dans différents lieux sécurisés qui ne sont connectés à aucun réseau. Il s'agit d'une bonne protection contre les pannes et les vulnérabilités informatiques, le vol et les erreurs humaines. À ce jour, cette approche requiert encore des connaissances techniques pour être réalisée correctement.
+ La valeur du Bitcoin est volatile
La valeur du Bitcoin est volatileLa valeur du Bitcoin peut augmenter ou diminuer de façon imprévisible sur une courte période de temps en raison de sa jeune économie, sa nature inusitée et ses marchés parfois peu liquides. En conséquence, conserver vos économies avec Bitcoin n'est pas recommandé. Bitcoin doit être considéré comme un actif à haut risque et vous ne devriez jamais stocker d'argent avec le Bitcoin que vous n'avez pas les moyens de perdre. Si vous recevez des paiements en Bitcoin, beaucoup de fournisseurs de services vous permettent de transférer vos Bitcoins instantanément dans votre devise.
+ + Les paiements Bitcoin sont irréversibles
Les paiements Bitcoin sont irréversiblesToute transaction effectuée avec Bitcoin ne peut être renversée. Elle peut seulement être remboursée par la personne recevant les fonds. Ce qui signifie que vous devez vous assurer de faire commerce avec des entreprises et des personnes que vous connaissez et en qui vous pouvez avoir confiance. Mais ne vous en faites pas, Bitcoin peut détecter les erreurs de frappe et ne vous laissera généralement pas envoyer d'argent vers une adresse invalide.
+ + Bitcoin n'est pas anonyme sans efforts
Bitcoin n'est pas anonyme sans effortsToutes les transactions Bitcoin sont stockées de façon publique et permanente sur le réseau. Ce qui signifie que quiconque peut consulter le solde et les transactions de chaque adresse Bitcoin. Toutefois, il n'est pas possible d'associer une adresse Bitcoin avec son propriétaire avant que celui-ci n'en ait fait la démonstration. Pour cette raison, il est recommandé d'utiliser différentes adresses Bitcoin. En fait, vous devriez en utiliser une nouvelle chaque fois que vous recevez un paiement. Cette pratique est spécialement importante pour les utilisations publiques comme les sites web. Vous pouvez aussi cacher l'adresse IP de votre ordinateur afin qu'elle ne puisse pas être enregistrée avec un outil tel que Tor.
+ + Bitcoin est encore expérimental
Bitcoin est encore expérimentalBitcoin est une nouvelle devise expérimentale qui est en développement actif. Bien qu'elle devienne de moins en moins expérimentale à chaque jour tandis que son usage augmente, vous devez garder en tête que le Bitcoin est une invention nouvelle qui joue sur un terrain qui n'a jamais été exploré à ce jour. En conséquence, son futur ne peut être prédit par personne.
+ + N'oubliez pas de payer vos taxes
N'oubliez pas de payer vos taxesBitcoin n'est pas une devise officielle. Ceci étant dit, la plupart des juridictions exigent tout de même que vous payiez des taxes sur le revenu, les ventes et les salaires sur tout ce qui a de la valeur, incluant le Bitcoin. Il est de votre responsabilité de vous informer et de vous conformer aux lois en application.
diff --git a/img/bitcoin-press.png b/img/bitcoin-press.png deleted file mode 100644 index a88bc133..00000000 Binary files a/img/bitcoin-press.png and /dev/null differ diff --git a/img/bubble.png b/img/bubble.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..8c2a61df Binary files /dev/null and b/img/bubble.png differ diff --git a/img/bubble.svg b/img/bubble.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..a41339cc --- /dev/null +++ b/img/bubble.svg @@ -0,0 +1,66 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/but_bitcoin.png b/img/but_bitcoin.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..f0e823bf Binary files /dev/null and b/img/but_bitcoin.png differ diff --git a/img/but_bitcoin.svg b/img/but_bitcoin.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..091d88f9 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/but_bitcoin.svg @@ -0,0 +1,64 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/but_involve.png b/img/but_involve.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..c5708175 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/but_involve.png differ diff --git a/img/but_involve.svg b/img/but_involve.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..e8c02f6a --- /dev/null +++ b/img/but_involve.svg @@ -0,0 +1,65 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/but_start.png b/img/but_start.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..4f35f2d5 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/but_start.png differ diff --git a/img/but_start.svg b/img/but_start.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..f8fd8b8a --- /dev/null +++ b/img/but_start.svg @@ -0,0 +1,62 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/but_warn.png b/img/but_warn.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..b7a2abc5 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/but_warn.png differ diff --git a/img/but_warn.svg b/img/but_warn.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..39d8c19f --- /dev/null +++ b/img/but_warn.svg @@ -0,0 +1,52 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/clients/armory.png b/img/clients/armory.png deleted file mode 100644 index 28b6bb04..00000000 Binary files a/img/clients/armory.png and /dev/null differ diff --git a/img/clients/bitcoin-qt.png b/img/clients/bitcoin-qt.png deleted file mode 100644 index e7c9e580..00000000 Binary files a/img/clients/bitcoin-qt.png and /dev/null differ diff --git a/img/clients/bitcoin-wallet.png b/img/clients/bitcoin-wallet.png deleted file mode 100644 index 33d53f8f..00000000 Binary files a/img/clients/bitcoin-wallet.png and /dev/null differ diff --git a/img/clients/electrum.png b/img/clients/electrum.png deleted file mode 100644 index b42d5a4a..00000000 Binary files a/img/clients/electrum.png and /dev/null differ diff --git a/img/clients/lo-armory.png b/img/clients/lo-armory.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..c30c9d5d Binary files /dev/null and b/img/clients/lo-armory.png differ diff --git a/img/clients/lo-bitcoin.png b/img/clients/lo-bitcoin.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..c075b8be Binary files /dev/null and b/img/clients/lo-bitcoin.png differ diff --git a/img/clients/lo-bitcoinwallet.png b/img/clients/lo-bitcoinwallet.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..a2edc75f Binary files /dev/null and b/img/clients/lo-bitcoinwallet.png differ diff --git a/img/clients/lo-blockchain.png b/img/clients/lo-blockchain.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..24ecf602 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/clients/lo-blockchain.png differ diff --git a/img/clients/lo-electrum.png b/img/clients/lo-electrum.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..d1f229ec Binary files /dev/null and b/img/clients/lo-electrum.png differ diff --git a/img/clients/lo-multibit.png b/img/clients/lo-multibit.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..46975f83 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/clients/lo-multibit.png differ diff --git a/img/clients/multibit.png b/img/clients/multibit.png deleted file mode 100644 index fed0bf47..00000000 Binary files a/img/clients/multibit.png and /dev/null differ diff --git a/img/ico-android.png b/img/dow-android.png similarity index 100% rename from img/ico-android.png rename to img/dow-android.png diff --git a/img/dow-ios.png b/img/dow-ios.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..03b6405e Binary files /dev/null and b/img/dow-ios.png differ diff --git a/img/ico-linux.png b/img/dow-linux.png similarity index 100% rename from img/ico-linux.png rename to img/dow-linux.png diff --git a/img/ico-osx-uni.png b/img/dow-osx-uni.png similarity index 60% rename from img/ico-osx-uni.png rename to img/dow-osx-uni.png index 0d266234..8aa0e4ba 100644 Binary files a/img/ico-osx-uni.png and b/img/dow-osx-uni.png differ diff --git a/img/dow-ubuntu.png b/img/dow-ubuntu.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..4e9fa265 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/dow-ubuntu.png differ diff --git a/img/dow-win.png b/img/dow-win.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..f6120d61 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/dow-win.png differ diff --git a/img/gravatar-140.png b/img/gravatar-140.png deleted file mode 100644 index 607e6e95..00000000 Binary files a/img/gravatar-140.png and /dev/null differ diff --git a/img/ico-ios.png b/img/ico-ios.png deleted file mode 100644 index 3f0c215e..00000000 Binary files a/img/ico-ios.png and /dev/null differ diff --git a/img/ico-mac.png b/img/ico-mac.png deleted file mode 100644 index 0205ab9c..00000000 Binary files a/img/ico-mac.png and /dev/null differ diff --git a/img/ico-ubuntu.png b/img/ico-ubuntu.png deleted file mode 100644 index bc129aac..00000000 Binary files a/img/ico-ubuntu.png and /dev/null differ diff --git a/img/ico-win.png b/img/ico-win.png deleted file mode 100644 index 7ffcea75..00000000 Binary files a/img/ico-win.png and /dev/null differ diff --git a/img/ico_anon.png b/img/ico_anon.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..40f5f8d4 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_anon.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_anon.svg b/img/ico_anon.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..237c1e04 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_anon.svg @@ -0,0 +1,75 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_conf.png b/img/ico_conf.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..097906a7 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_conf.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_conf.svg b/img/ico_conf.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..82fac393 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_conf.svg @@ -0,0 +1,133 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_democracy.png b/img/ico_democracy.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..7039487f Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_democracy.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_democracy.svg b/img/ico_democracy.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..cb69a2de --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_democracy.svg @@ -0,0 +1,65 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_donate.png b/img/ico_donate.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..f52bcf01 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_donate.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_donate.svg b/img/ico_donate.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..bbaf5f17 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_donate.svg @@ -0,0 +1,74 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_fast.png b/img/ico_fast.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..1759b836 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_fast.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_fast.svg b/img/ico_fast.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..da5ed6ec --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_fast.svg @@ -0,0 +1,107 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_help.png b/img/ico_help.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..6c6b5065 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_help.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_help.svg b/img/ico_help.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..493933ef --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_help.svg @@ -0,0 +1,73 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_international.png b/img/ico_international.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..27418f59 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_international.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_international.svg b/img/ico_international.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..bf624e58 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_international.svg @@ -0,0 +1,109 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_invoice.png b/img/ico_invoice.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..0b96cf5d Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_invoice.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_invoice.svg b/img/ico_invoice.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..88f7c560 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_invoice.svg @@ -0,0 +1,74 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_irreversible.png b/img/ico_irreversible.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..100e309c Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_irreversible.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_irreversible.svg b/img/ico_irreversible.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..a0a87a1a --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_irreversible.svg @@ -0,0 +1,77 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_key.png b/img/ico_key.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..d64b486d Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_key.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_key.svg b/img/ico_key.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..31811ff2 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_key.svg @@ -0,0 +1,85 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_lab.png b/img/ico_lab.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..b0ade809 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_lab.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_lab.svg b/img/ico_lab.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..714d19e4 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_lab.svg @@ -0,0 +1,71 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_lock.png b/img/ico_lock.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..968fa2de Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_lock.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_lock.svg b/img/ico_lock.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..926fe703 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_lock.svg @@ -0,0 +1,72 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_lowfee.png b/img/ico_lowfee.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..3b97638b Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_lowfee.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_lowfee.svg b/img/ico_lowfee.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..276e6b8e --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_lowfee.svg @@ -0,0 +1,81 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_market.png b/img/ico_market.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..65dcc7a2 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_market.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_market.svg b/img/ico_market.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..4c50f123 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_market.svg @@ -0,0 +1,67 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_micro.png b/img/ico_micro.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..b46fc496 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_micro.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_micro.svg b/img/ico_micro.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..77692774 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_micro.svg @@ -0,0 +1,77 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_mobile.png b/img/ico_mobile.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..73eb153d Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_mobile.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_mobile.svg b/img/ico_mobile.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..8dedd812 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_mobile.svg @@ -0,0 +1,87 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_multi.png b/img/ico_multi.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..cd04fcac Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_multi.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_multi.svg b/img/ico_multi.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..0c373d87 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_multi.svg @@ -0,0 +1,77 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_network.png b/img/ico_network.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..6df8bcbb Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_network.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_network.svg b/img/ico_network.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..aec53e57 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_network.svg @@ -0,0 +1,112 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_own.png b/img/ico_own.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..d9c170f0 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_own.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_own.svg b/img/ico_own.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..89ff8e67 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_own.svg @@ -0,0 +1,65 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_pci.png b/img/ico_pci.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..a780cd14 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_pci.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_pci.svg b/img/ico_pci.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..d83f7bcd --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_pci.svg @@ -0,0 +1,94 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_shield.png b/img/ico_shield.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..fd35a64d Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_shield.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_shield.svg b/img/ico_shield.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..624fb363 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_shield.svg @@ -0,0 +1,256 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_simple.png b/img/ico_simple.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..fe669262 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_simple.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_simple.svg b/img/ico_simple.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..69fbeb6a --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_simple.svg @@ -0,0 +1,65 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_software.png b/img/ico_software.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..0e34034d Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_software.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_software.svg b/img/ico_software.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..5df6340e --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_software.svg @@ -0,0 +1,65 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_solve.png b/img/ico_solve.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..ebcca130 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_solve.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_solve.svg b/img/ico_solve.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..3999b240 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_solve.svg @@ -0,0 +1,71 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_spread.png b/img/ico_spread.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..17c7950c Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_spread.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_spread.svg b/img/ico_spread.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..7851e27f --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_spread.svg @@ -0,0 +1,83 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_translate.png b/img/ico_translate.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..cd312f11 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_translate.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_translate.svg b/img/ico_translate.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..3696b51a --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_translate.svg @@ -0,0 +1,105 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_transparency.png b/img/ico_transparency.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..3e18e180 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_transparency.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_transparency.svg b/img/ico_transparency.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..002ec35d --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_transparency.svg @@ -0,0 +1,75 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_visib.png b/img/ico_visib.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..60d1d5aa Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_visib.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_visib.svg b/img/ico_visib.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..86acb763 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_visib.svg @@ -0,0 +1,65 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/ico_wiki.png b/img/ico_wiki.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..95924b4d Binary files /dev/null and b/img/ico_wiki.png differ diff --git a/img/ico_wiki.svg b/img/ico_wiki.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..5d8e49a1 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/ico_wiki.svg @@ -0,0 +1,266 @@ + + + + diff --git a/img/icon-be-the-network.png b/img/icon-be-the-network.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..92ba7125 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/icon-be-the-network.png differ diff --git a/img/icon-be-the-network.svg b/img/icon-be-the-network.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..eab1a856 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/icon-be-the-network.svg @@ -0,0 +1,318 @@ + + + + diff --git a/lib/innerbg.png b/img/innerbg.png similarity index 100% rename from lib/innerbg.png rename to img/innerbg.png diff --git a/img/logo_bitcoin_foundation.png b/img/logo_bitcoin_foundation.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..d3ca68aa Binary files /dev/null and b/img/logo_bitcoin_foundation.png differ diff --git a/img/logo_small.png b/img/logo_small.png deleted file mode 100644 index e69f960b..00000000 Binary files a/img/logo_small.png and /dev/null differ diff --git a/img/logotop.png b/img/logotop.png new file mode 100644 index 00000000..dd828830 Binary files /dev/null and b/img/logotop.png differ diff --git a/img/logotop.svg b/img/logotop.svg new file mode 100644 index 00000000..dc64d878 --- /dev/null +++ b/img/logotop.svg @@ -0,0 +1,135 @@ + + + + diff --git a/index.html b/index.html index af2d636c..9abb2c39 100644 --- a/index.html +++ b/index.html @@ -1,159 +1,16 @@ --- -layout: index -section: index -title: P2P digital currency -DOWNLOAD_VERSION: 0.8.1 -ALERT_CLASS: -ALERT: --- -- Bitcoin is an experimental new digital currency that enables instant payments to anyone, anywhere in the world. - Bitcoin uses peer-to-peer technology to operate with no central authority: managing transactions and issuing money are carried out collectively by the network. - Bitcoin is also the name of the open source software which enables the use of this currency. -
-The software is a community-driven open source project, released under the MIT license.
-- Learn how to use Bitcoin » - - Learn more about Bitcoin » -
-
- Latest Bitcoin-Qt version: {{ page.DOWNLOAD_VERSION }}
-
- (see all Bitcoin clients)
-
 Windows (zip) ~13MB
-
Windows (zip) ~13MB
-  Windows (exe) ~9MB
-
Windows (exe) ~9MB
-  Ubuntu PPA
-
Ubuntu PPA
-  Linux (tgz, 32/64-bit) ~12MB
-
Linux (tgz, 32/64-bit) ~12MB
-  Mac OS X ~13MB
-
Mac OS X ~13MB
- Press mailing list for presentation and interview requests: 
{{ post.date | date:"%e %B %Y" }}
- {% if post.src %} - - {% endif %} - {{ post.content }} - {% endfor %} - -